Node Styles
Nodes are rendered using INodeStyle implementations. yFiles for HTML provides a selection of predefined node styles.
Styles that support a border Stroke and background Fill and a predefined or custom shape are: ShapeNodeStyle, RectangleNodeStyle, ArrowNodeStyle, GeneralPathNodeStyle, and GroupNodeStyle.
Furthermore, it is possible to create custom visualizations using delegating styles, composing styles, or an abstract base implementation.
Predefined Shapes
With the ShapeNodeStyle, you can easily display predefined shapes such as rectangles and triangles. The style supports both a background fill and a border stroke. You can specify the desired shape using the shape property.
graph.createNode(
[0, 0, 100, 60],
new ShapeNodeStyle({
fill: 'orange',
stroke: 'black',
shape: 'rectangle'
})
)The ShapeNodeStyle provides many predefined, general shapes and serves as a versatile base visualization for graph nodes. It is often used in adapter classes for labels and ports (see Using Node Styles for Labels and Ports) or for customizing selection, focus, and highlight.
| Name | Visualization |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
By default, the shapes are stretched to fit the node’s layout.
Setting keepIntrinsicAspectRatio to true forces the shapes to maintain their original aspect ratios (typically 1:1 for most shapes) within the node’s layout.
For example, the shape ELLIPSE is rendered as a circle in this case.
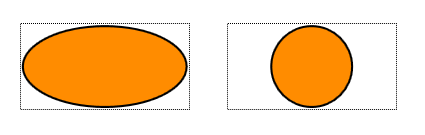
false (left) and true (right).Images
yFiles for HTML can use images to render nodes. The ImageNodeStyle class uses an SVG <image> element to render the node.
Besides the href, ImageNodeStyle offers settings to specify the aspect ratio and to define an optional normalizedOutline.
const imageUrl = './resources/yFiles.svg'
// determine the intrinsic aspect ratio of the image
const imageAspectRatio = await ImageNodeStyle.getAspectRatio(imageUrl)
// the outline of the image between 0 and 1
const outlinePath = new GeneralPath()
outlinePath.appendEllipse(new Rect(0, 0, 1, 1), true)
const node = graph.createNode(
[0, 0, 50, 50],
new ImageNodeStyle({
href: imageUrl,
aspectRatio: imageAspectRatio,
normalizedOutline: outlinePath
})
)
0 (left) and 1 (right).The optional normalizedOutline can be used to refine the behavior such as hit tests or edge cropping. The shape itself is not visualized.
Polygons
The GeneralPathNodeStyle supports using arbitrary polygons to visually represent a node. Similar to other shape-based styles, the GeneralPathNodeStyle supports a background fill and an outline stroke.
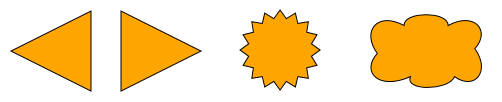
const triangleLeft = new GeneralPath()
triangleLeft.moveTo(0.0, 0.5)
triangleLeft.lineTo(1.0, 0.0)
triangleLeft.lineTo(1.0, 1.0)
triangleLeft.close()
graph.createNode(
new Rect(0, 0, 80.0, 80.0),
new GeneralPathNodeStyle({
fill: 'orange',
path: triangleLeft
})
)
const triangleRight = new GeneralPath()
triangleRight.moveTo(1.0, 0.5)
triangleRight.lineTo(0.0, 1.0)
triangleRight.lineTo(0.0, 0.0)
triangleRight.close()
graph.createNode(
new Rect(110, 0, 80.0, 80.0),
new GeneralPathNodeStyle({
fill: 'orange',
path: triangleRight
})
)
const starPath = GeneralPathNodeStyle.createStarPath(16, 0.8)
graph.createNode(
new Rect(220, 0, 100.0, 80.0),
new GeneralPathNodeStyle({
fill: 'orange',
path: starPath
})
)
const cloudPath = new GeneralPath()
// ...
graph.createNode(
new Rect(350, 0, 130.0, 80),
new GeneralPathNodeStyle({
fill: 'orange',
path: cloudPath
})
)The style’s properties and their effects are:
- path
-
Defines the boundary of the path.
- aspectRatio
-
Defines the aspect ratio for scaling the path to a node’s size.
- fill
-
Defines how the path is filled.
- stroke
-
Defines how the outline is drawn.
Rectangles
The RectangleNodeStyle uses a rectangular shape as its foundation and supports configurable round or diagonal corners. Similar to other shape-based styles, the RectangleNodeStyle supports a background fill and an outline stroke.
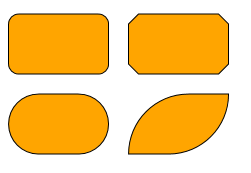
graph.createNode(
[0, 0, 100, 60],
new RectangleNodeStyle({
cornerSize: 10,
cornerStyle: 'round',
fill: 'orange',
stroke: 'black'
})
)
graph.createNode(
[120, 0, 100, 60],
new RectangleNodeStyle({
cornerSize: 10,
cornerStyle: 'cut',
fill: 'orange',
stroke: 'black'
})
)
graph.createNode(
[0, 80, 100, 60],
new RectangleNodeStyle({
cornerSize: 0.5,
scaleCornerSize: true,
cornerStyle: 'round',
fill: 'orange',
stroke: 'black'
})
)
graph.createNode(
[120, 80, 100, 60],
new RectangleNodeStyle({
cornerSize: 1,
scaleCornerSize: true,
cornerStyle: 'round',
corners: ['top-left', 'bottom-right'],
fill: 'orange',
stroke: 'black'
})
)The style’s properties and their effects are:
- cornerSize
-
The size of the corners. Depending on scaleCornerSize, this is either an absolute value or a ratio between 0 and 1.
- scaleCornerSize
-
If set to
true, the value of cornerSize is interpreted as a ratio between 0 and 1. Otherwise, it is interpreted as an absolute value. This mainly affects how the shape looks when the node is resized.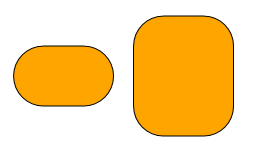 scaleCornerSize =
scaleCornerSize =false, cornerSize =30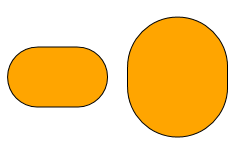 scaleCornerSize =
scaleCornerSize =true, cornerSize =0.5 - cornerStyle
-
Configures how the corners are drawn, either as round corners or straight line.
 ROUND
ROUND CUT
CUT - corners
-
Configures which corners are affected. By default, all corners are affected. Note that all affected corners share the same corner style and size.
 ALL (the default)
ALL (the default) TOP
TOP TOP_LEFT, BOTTOM_RIGHT
TOP_LEFT, BOTTOM_RIGHTWhen corners do not meet, for example, in the second and third example above, the corner size may extend all the way to the other side of the node.
- fill
-
Defines how the shape is filled.
- stroke
-
Defines how the outline is drawn.
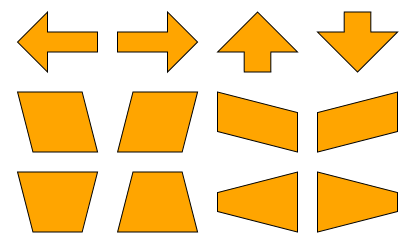
Arrow Shapes
The ArrowNodeStyle renders nodes as arrows. It supports different kinds of arrow shapes with a configurable angle for the arrowhead and a configurable shaft thickness. Similar to all shape-based node styles, the ArrowNodeStyle supports setting a border stroke and background fill.
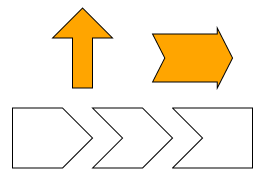
graph.createNode(
[0, -20, 60, 80],
new ArrowNodeStyle({
direction: 'up',
fill: 'orange',
stroke: 'black'
})
)
graph.createNode(
[100, 0, 80, 60],
new ArrowNodeStyle({
shape: 'notched-arrow',
shaftRatio: 0.8,
angle: 0.15 * Math.PI,
fill: 'orange',
stroke: 'black'
})
)
graph.createNode(
[-40, 80, 80, 60],
new ArrowNodeStyle({
shape: 'arrow',
shaftRatio: 1.0,
angle: Math.PI * 0.25,
direction: 'right'
})
)
graph.createNode(
[40, 80, 80, 60],
new ArrowNodeStyle({
shape: 'notched-arrow',
shaftRatio: 1.0,
angle: Math.PI * 0.25,
direction: 'right'
})
)
graph.createNode(
[120, 80, 80, 60],
new ArrowNodeStyle({
shape: 'arrow',
shaftRatio: 1.0,
angle: -Math.PI * 0.25,
direction: 'left'
})
)Shape
The ArrowNodeStyle can render different arrow shapes. These are defined in the ArrowStyleShape enumeration and can be set using the shape property.
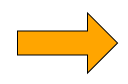

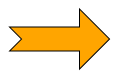
ArrowNodeStyle also supports some shapes that are not typical arrows. These are discussed in more detail below.


Angle and Thickness
Aside from the shape the appearance of an arrow is defined by the thickness of its shaft and the angle of its head.
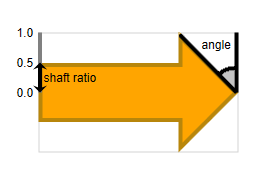
The thickness of the arrow shaft can be set with the shaftRatio property. It is defined as a ratio between 0 and 1.
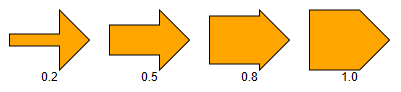
The size of the head is determined by its angle. The angle is measured in radians and can be set using the angle property. Values between 0 and π / 2 are supported.
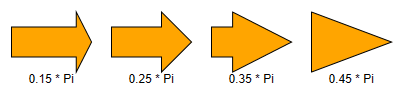
At shaftRatio 1 the angle property also supports negative values.
This allows for rendering concave shapes.
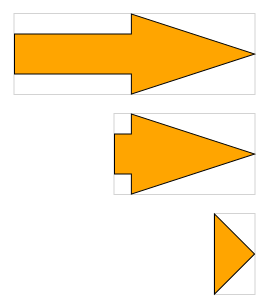
Note that the arrowhead will always spread the full height of the node for horizontal arrows or the full width for vertical arrows. If this is not possible with the set angle, then the angle is capped to the largest value which meets this requirement, as shown in the bottommost image of the figure below.
Direction
The arrow shape can be rotated to point in the four major directions LEFT, RIGHT, UP, and DOWN using the direction property.
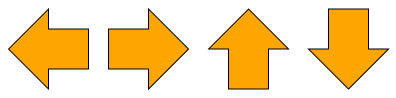
Trapezoid and Parallelogram
The shapes PARALLELOGRAM and TRAPEZOID are not arrow shapes in the proper sense. However, they technically behave like arrow shapes: they have an angled side and exhibit a similar resizing behavior. The shaftRatio property has no effect on these shapes and is ignored.
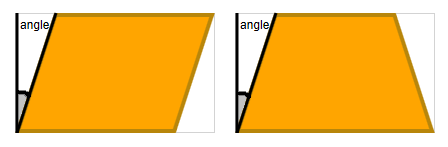
The trapezoid’s direction is chosen in a way that stretching the shape at the parallel sides keeps the angle stable. Therefore, with direction RIGHT the small side of the trapezoid points upwards.
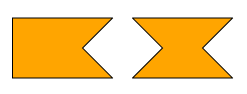
The parallelogram is symmetric to 180° rotation. To get a mirrored parallelogram, choose a negative angle

Groups and Folders
GroupNodeStyle is a style primarily intended for group and folder nodes (i.e., collapsed group nodes). This style creates visualizations similar to tabbed file folders. Like all shape-based node styles, GroupNodeStyle supports setting a border using stroke. Additionally, there are several properties for coloring specific areas in a GroupNodeStyle.
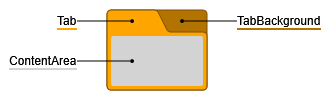
The cssClass property enables support for CSS classes on the style. The given CSS class is
applied to the root <g> element, and the GroupNodeStyle implicitly adds more specific CSS classes, prefixed
with yfiles-, to all distinctive parts of its visualization.
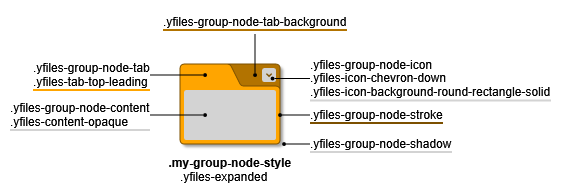
The described CSS classes above only depict the current state of shown node. You can find more details on the available CSS classes in the following subsections and general information about CSS item styling with yFiles for HTML in CSS Item Styles.
Aside from its coloring properties, GroupNodeStyle offers many configuration options for fine-grained control over tab position, shape, and size.
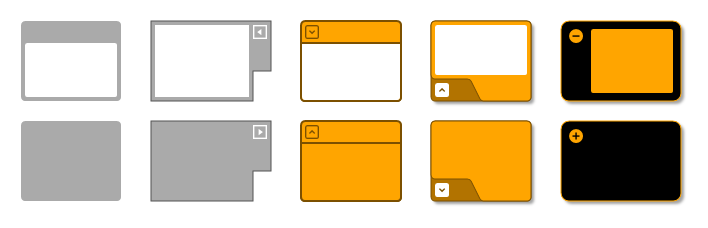
graph.setStyle(groupNode1, new GroupNodeStyle())
graph.setStyle(
groupNode2,
new GroupNodeStyle({
cornerRadius: 0,
groupIcon: 'triangle-left',
iconPosition: 'leading',
iconBackgroundShape: 'square',
iconForegroundFill: 'white',
tabSlope: 0,
tabPosition: 'right-leading',
stroke: 'black'
})
)
graph.setStyle(
groupNode3,
new GroupNodeStyle({
groupIcon: 'chevron-down',
iconBackgroundShape: 'round-rectangle',
iconBackgroundFill: 'darkRed',
iconForegroundFill: 'black',
iconPosition: 'leading',
iconOffset: 3,
tabPosition: 'top-trailing',
tabFill: 'orange',
tabBackgroundFill: 'orange',
tabPadding: 1,
tabHeight: 22,
tabWidth: 0,
stroke: 'black'
})
)
graph.setStyle(
groupNode4,
new GroupNodeStyle({
drawShadow: true,
groupIcon: 'chevron-up',
iconForegroundFill: 'black',
iconPosition: 'leading',
tabPosition: 'bottom-trailing',
tabFill: 'orange',
tabBackgroundFill: 'black',
tabHeight: 22,
tabSlope: 0.5,
stroke: 'black'
})
)
graph.setStyle(
groupNode5,
new GroupNodeStyle({
cornerRadius: 8,
contentAreaFill: 'orange',
drawShadow: true,
groupIcon: 'minus',
iconPosition: 'leading',
iconBackgroundFill: 'orange',
iconForegroundFill: 'black',
iconBackgroundShape: 'circle-solid',
tabPosition: 'left',
tabFill: 'black',
tabHeight: 22,
tabSlope: 0.5,
tabPadding: 8,
stroke: 'orange'
})
)
graph.setStyle(
folderNode1,
new GroupNodeStyle({
folderIcon: 'none'
})
)
graph.setStyle(
folderNode2,
new GroupNodeStyle({
cornerRadius: 0,
groupIcon: 'triangle-left',
folderIcon: 'triangle-right',
iconPosition: 'leading',
iconBackgroundShape: 'square',
iconForegroundFill: 'white',
tabPosition: 'right-leading',
tabSlope: 0,
stroke: 'black'
})
)
graph.setStyle(
folderNode3,
new GroupNodeStyle({
groupIcon: 'chevron-down',
folderIcon: 'chevron-up',
iconBackgroundShape: 'round-rectangle',
iconBackgroundFill: 'darkRed',
iconForegroundFill: 'black',
iconPosition: 'leading',
iconOffset: 3,
tabPosition: 'top-trailing',
tabFill: 'orange',
tabBackgroundFill: 'orange',
tabPadding: 1,
tabHeight: 22,
tabWidth: 0,
stroke: 'black'
})
)
graph.setStyle(
folderNode4,
new GroupNodeStyle({
drawShadow: true,
groupIcon: 'chevron-up',
folderIcon: 'chevron-down',
iconForegroundFill: 'black',
iconPosition: 'leading',
tabPosition: 'bottom-trailing',
tabFill: 'orange',
tabBackgroundFill: 'black',
tabHeight: 22,
tabSlope: 0.5,
stroke: 'black'
})
)
graph.setStyle(
folderNode5,
new GroupNodeStyle({
cornerRadius: 8,
contentAreaFill: 'orange',
drawShadow: true,
groupIcon: 'minus',
iconPosition: 'leading',
iconBackgroundFill: 'orange',
iconForegroundFill: 'black',
iconBackgroundShape: 'circle-solid',
tabPosition: 'left',
tabFill: 'black',
tabHeight: 22,
tabSlope: 0.5,
tabPadding: 8,
stroke: 'orange'
})
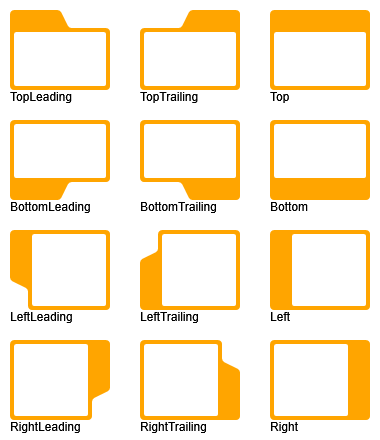
)Tab Position, Shape, and Size
The enumeration GroupNodeStyleTabPosition defines several tab positions for GroupNodeStyle, which
can be set using the tabPosition property.
If the cssClass property is defined, each position also sets a CSS class like yfiles-tab-<position>, for example yfiles-tab-top-leading.
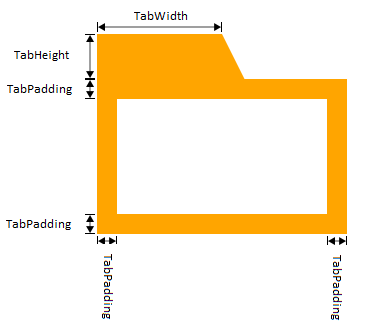
Properties tabWidth, tabHeight, tabPadding, and tabSlope determine the shape and size of the tab.
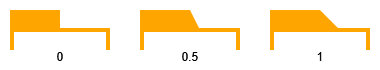
|
Note
|
tabWidth and tabSlope are ignored if tabPosition is neither a leading nor a trailing position. In Supported tab positions, this can be observed for positions TOP, BOTTOM, LEFT, and RIGHT. |
Group and Folder Icon
GroupNodeStyle supports drawing an interactive handle for
toggling the expansion state of a group node. The style offers several
properties for configuring the position and the look of the handle and multiple CSS classes if the
cssClass property is defined. The container element in general holds the yfiles-group-node-icon
CSS class with more specific classes depending on the actual icon.
The enumeration GroupNodeStyleIconType defines different icon types for the visualization of the handle that come
with a CSS class like yfiles-icon-<type>, for example yfiles-icon-chevron-up.
GroupNodeStyle supports different types of icons depending on the expansion state of its node. Property folderIcon determines which icon to show for collapsed nodes. Conversely, property groupIcon determines the icon for expanded nodes.
Moreover, there are several additional properties for controlling the look of the icon that are independent of expansion state.
iconBackgroundShape governs the background shape of the icon, and the
GroupNodeStyleIconBackgroundShape enumeration defines supported shape types and comes with CSS classes like
yfiles-icon-background-<shape>, for example yfiles-background-circle.
Of course, icon background and
icon foreground can be set individually or styled with the
yfiles-icon-background and yfiles-icon-foreground CSS classes if the cssClass property
is defined.
The position of the icon is controlled with iconPosition and iconOffset (together with properties tabPosition and tabPadding). The position of the icon is anchored to two sides of the corresponding node. tabPosition determines the first side, and iconPosition the second side. The sum of tabPadding and iconOffset is the distance from the icon to the two anchor sides.
Finally, the size of the icon can be set using iconSize.
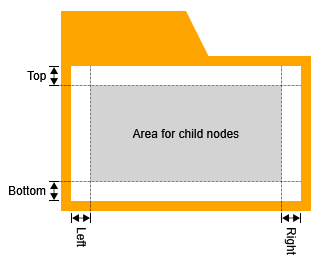
Content Area
For expanded groups, the style’s content area holds the child nodes of the group. Its padding (together with the tabPadding) determines how close child nodes can be moved to the border of their parent node.
For easier interaction with child nodes of expanded groups, the behavior of hit tests, marquee selection tests, and lasso selection tests in the content area can be changed. By default, the aforementioned tests treat the content area in the same way as any other part of the node. If hitTransparentContentArea is enabled, the content area is treated as if it was not part of any node. In this state, it is, for example, possible to start a marquee selection inside the content area for easy selection of child nodes without selecting the parent node, too.
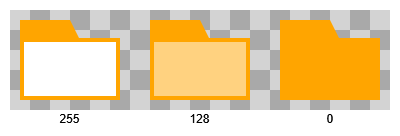
There are two rendering modes for the content area. By default, it is rendered over the tab and tab background:
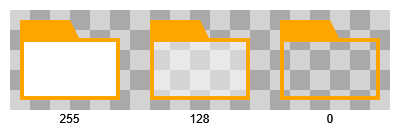
If renderTransparentContentArea is enabled, neither the tab nor the tab background are rendered below the content area:
For collapsed groups, the content area visualization can be turned off through property showFolderContentArea.
If the cssClass property is defined, the style also creates CSS classes for the different areas and states:
-
yfiles-expandedoryfiles-collapsed: On the root container of the group visualization. -
yfiles-group-node-content: General CSS class for the content area. -
yfiles-content-opaqueoryfiles-content-transparent: Additional class on the content area, depending on hitTransparentContentArea.
Corner Radius and Drop Shadow
The corners of a GroupNodeStyle's shape can be rounded off using property cornerRadius.
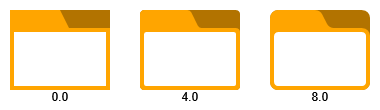
Finally, GroupNodeStyle can render a drop shadow if drawShadow is enabled.

Tab Labels
One common use case for GroupNodeStyle's tabbed file folder visualization is displaying text in the tab or the tab background of the visualization. GroupNodeStyle supports this use case with the help of class GroupNodeLabelModel. The model’s tab parameter places labels in the tab, and its tab background parameter places labels in the tab background.
Additionally, property tabSizePolicy determines if the preferred sizes of tab (and tab background) labels affect the size of the tab. By default, this is not the case.
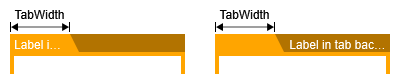
However, using value ADJUST_TO_LABEL, the width of the tab may grow beyond or shrink below GroupNodeStyle's tabWidth to accommodate a tab label or a tab background label.
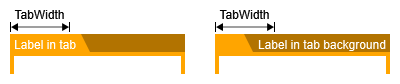
Size Constraints
By default, GroupNodeStyle constrains the minimum size of the node to ensure that the tab, as well as the icon, are visible. This means that the group cannot shrink below the size of the tab and the icon if they are displayed at all.
Additionally, you can configure the minimum size of the content area with the property minimumContentAreaSize. This value defines the minimum size of the content area, i.e., the part of the group that contains the child nodes. This minimum size includes the contentAreaPadding.
Using other Node Styles for Groups and Folders
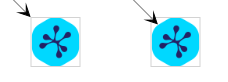
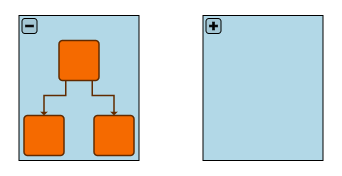
In addition to the GroupNodeStyle, yFiles for HTML offers the CollapsibleNodeStyleDecorator to represent group and folder nodes. The CollapsibleNodeStyleDecorator is a special node style that decorates any other node style with an interactive handle for toggling the expansion state of a group node.
By default, this handle is rendered as a plus sign (+) when in the collapsed
state and a minus sign (-) when in the expanded state. The following sample shows the group node
representation for a group node with three child nodes and a collapsed group node side by side:
The CollapsibleNodeStyleDecorator provides several properties to control the location of the toggle handle. The visualization of the handle can be changed by overriding createButton.
The following example presents the setup for the group node style shown above. The handle is placed with some distance from the top left corner of the node. The padding ensures that the upper area containing the handle is not overlapped by the content of the group.
// create the style to decorate
const decoratedStyle = new ShapeNodeStyle({
shape: 'rectangle',
fill: 'lightblue'
})
// decorate the style and set as default style for group nodes
foldingManager.masterGraph.groupNodeDefaults.style =
new CollapsibleNodeStyleDecorator({
wrappedStyle: decoratedStyle,
buttonPlacement: new FreeNodeLabelModel().createParameter({
layoutRatio: [0, 0],
layoutOffset: [3, 3],
labelRatio: [0, 0]
}),
padding: [25, 5, 5, 5]
})|
Note
|
CollapsibleNodeStyleDecorator needs to be set to the group node in the master graph. |
The representations of a group node’s collapsed state and expanded state can be different. By default, however, the initial style that is used to render a folder node in a folding view is the style of the original (expanded) group node from the master graph. See the section Maintaining the Folder Node State for details.
Custom Styles
yFiles for HTML offers an abstract style implementation: NodeStyleBase<TVisual>. Creating custom styles using this class as a base is discussed in detail in section Customizing Styles.
Invisible Nodes
The INodeStyle.VOID_NODE_STYLE can be used to make a node invisible while still keeping it in the graph. Additionally, the node will not respond to any user interactions, such as mouse clicks.
graph.setStyle(invisibleNode, INodeStyle.VOID_NODE_STYLE)