| Chapter 10. Settings Dialogs and Components | ||
|---|---|---|
| Prev | Next | |
Table of Contents
This chapter discusses GUI utility functionality that provides means to quickly create property editors for items of diverse types.
The classes from package
y.option![]() constitute a framework to conveniently handle property management and
manipulation.
It offers support for internationalization and localization of dialogs
(i18n/l10n for short), as well as (de)serialization of settings.
The framework separates responsibilities applying a Model-Delegate pattern,
which facilitates, for example, different styles of settings presentations and
manipulation.
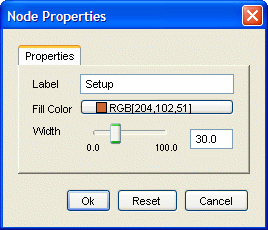
Figure 10.1, “Dialog-based and table-based settings presentation” shows the alternative presentation styles.
constitute a framework to conveniently handle property management and
manipulation.
It offers support for internationalization and localization of dialogs
(i18n/l10n for short), as well as (de)serialization of settings.
The framework separates responsibilities applying a Model-Delegate pattern,
which facilitates, for example, different styles of settings presentations and
manipulation.
Figure 10.1, “Dialog-based and table-based settings presentation” shows the alternative presentation styles.
Figure 10.1. Dialog-based and table-based settings presentation
 |
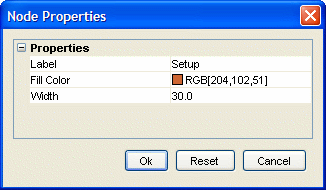 |
| Dialog-based and... | table-based settings presentation. |
The separation also permits the use of multiple dialogs (in other words, multiple views) to present and modify settings that are managed by a common model. Synchronization of model and view(s) is covered by different policies, following "push" and "pull" semantics.
The classes from package y.option reflect a modification of the Model-View-Controller (MVC) paradigm, dubbed Model-Delegate pattern. Two of the three responsibilities from MVC, namely the view and controller part, are brought together in a so-called User Interface (UI) Delegate. Hence classes with the following roles can be distinguished:
In terms of MVC then, class OptionHandler![]() together with classes OptionItem
together with classes OptionItem![]() and
OptionSection
and
OptionSection![]() make up the model which
holds the data.
The view/controller part is in the implementations of interface
Editor
make up the model which
holds the data.
The view/controller part is in the implementations of interface
Editor![]() .
.
Figure 10.2, “Settings framework core classes” shows the essential classes of the settings framework.
|
Copyright ©2004-2012, yWorks GmbH. All rights reserved. |