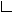 y.layout.tabular.TabularLayouter
y.layout.tabular.TabularLayouter
|
Search this API | ||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | ||||||||
| SUMMARY: NESTED | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | ||||||||
java.lang.Objecty.layout.tabular.TabularLayouter
public class TabularLayouter
This layout algorithm places nodes in a tabular fashion.
The nodes are placed based on an underlying PartitionGrid structure.
Only nodes are arranged, edges are not routed, but their bend points are cleared.
Therefore, this algorithm is suitable if nodes should be arranged in rows and columns in a regular fashion.
A tabular layout of 8 nodes organized in a 3x3 grid
![]()
A tabular layout of 8 nodes organized in a 2x6 grid with some gaps (empty cells)
The table consists of cells which form rows and
columns. Each cell contains a single node or might also be empty.
Note that it is not required that the input graph already contains a PartitionGrid for this algorithm
to properly work. It is, however, useful if the resulting row and column geometry should be retrieved
(e.g. to visualize the table).
It is mandatory to register a PartitionGrid when using layout policy LAYOUT_POLICY_FIXED_SIZE.
Rows/columns do not overlap and are not compacted: nodes that belong to different rows are strictly separated with respect to the covered y-coordinates range and nodes that belong to different columns are strictly separated with respect to the covered x-coordinate range.
It is possible to define in which cell of the table a certain node should be placed when using
policy LAYOUT_POLICY_FIXED_SIZE. See the policy documentation for more details.
The algorithm considers the following properties associated with RowDescriptors and
ColumnDescriptors of a PartitionGrid registered with the input graph:
RowDescriptor.getTopInset()
RowDescriptor.getBottomInset()
RowDescriptor.getMinimumHeight()
ColumnDescriptor.getLeftInset()
ColumnDescriptor.getRightInset()
ColumnDescriptor.getMinimumWidth()
Group nodes are supported but only top-level groups are handled like an actual node in the table.
The content of top-level groups is kept fix. That means that the content
keeps the relative location with respect to the top-level group but it is not recursively arranged in
a tabular fashion. To achieve recursive layouts where the content is a tabular layout too, use
RecursiveGroupLayouter with TabularLayouter as core layout algorithm.
Generally, it is recommended that group nodes already have proper bounds enclosing all content (and their labels).
Otherwise, overlaps may occur, as group node sizes are not changed by this algorithm.
RecursiveGroupLayouter with RecursiveGroupLayouter.NULL_LAYOUTER
as core algorithm can be used to recursively assign group node sizes.
NodeHalos.PartitionGrid.isRowOrderOptimizationEnabled() and
PartitionGrid.isColumnOrderOptimizationEnabled() of a given grid instance are not
considered by this layout algorithm. Furthermore, the following properties of rows and columns
are ignored as well: RowDescriptor.getTightness(), RowDescriptor.isIndexFixed(),
ColumnDescriptor.getTightness() and ColumnDescriptor.isIndexFixed().PartitionGrid |
 |
 |
 |
| Field Summary | |
|---|---|
static byte |
LAYOUT_POLICY_AUTO_SIZE
Layout policy that automatically chooses the table size of the layout. |
static byte |
LAYOUT_POLICY_FIXED_SIZE
Layout policy that adopts the size from an already registered PartitionGrid instance. |
static byte |
LAYOUT_POLICY_FROM_SKETCH
Layout policy that uses the coordinates of the input graph to determine the table size and the mapping of the nodes to the cells. |
static java.lang.Object |
NODE_LAYOUT_DESCRIPTOR_DPKEY
A DataProvider key for providing layout information for each node
|
| Fields inherited from interface y.layout.Layouter |
|---|
EDGE_ID_DPKEY, NODE_ID_DPKEY, NODE_TYPE_DPKEY, SELECTED_EDGES, SELECTED_NODES |
| Constructor Summary | |
|---|---|
TabularLayouter()
|
|
| Method Summary | |
|---|---|
boolean |
canLayout(LayoutGraph graph)
Accepts all general graphs. |
void |
doLayout(LayoutGraph graph)
Arranges the input graph in a tabular fashion. |
NodeLayoutDescriptor |
getDefaultNodeLayoutDescriptor()
Returns the NodeLayoutDescriptor instance used for all the nodes that do not have an individual
layout descriptor. |
byte |
getLayoutPolicy()
Returns the policy defining the size of the resulting tabular layout and the mapping of the nodes to the table cells. |
java.util.Comparator |
getNodeComparator()
Returns the Comparator that defines the order in which the free nodes are placed in the table. |
boolean |
isNodeLabelConsiderationEnabled()
Returns whether or not the layout algorithm reserves space for node labels. |
void |
setDefaultNodeLayoutDescriptor(NodeLayoutDescriptor descriptor)
Specifies the NodeLayoutDescriptor instance used for all the nodes that do not have an individual
layout descriptor. |
void |
setLayoutPolicy(byte layoutPolicy)
Specifies the policy defining the size of the resulting tabular layout and the mapping of the nodes to the table cells. |
void |
setNodeComparator(java.util.Comparator comp)
Specifies the Comparator that defines the order in which the free nodes are placed in the table. |
void |
setNodeLabelConsiderationEnabled(boolean nodeLabelConsiderationEnabled)
Specifies whether or not the layout algorithm reserves space for node labels. |
| Methods inherited from class java.lang.Object |
|---|
clone, equals, finalize, getClass, hashCode, notify, notifyAll, toString, wait, wait, wait |
| Field Detail |
|---|
public static final java.lang.Object NODE_LAYOUT_DESCRIPTOR_DPKEY
DataProvider key for providing layout information for each node
public static final byte LAYOUT_POLICY_AUTO_SIZE
The resulting table gets a dimension such that both row count and column count are similar, leading to a maximally square table with respect to the row and column count (actual node sizes are not considered). For example, given a graph with 14 nodes, a 4x4 grid will be created.
The nodes are arranged in the table in a row-wise fashion using the order
provided by getNodeComparator().
PartitionGrid instance to get the computed location and the dimension
of the table after the layout run. To do so query the according values from the
RowDescriptors and ColumnDescriptors associated with the grid.PartitionGrid instance is registered that already contains rows
and/or columns, the number of rows/columns is ignored and,
furthermore, the list of rows will be cleared. However, the settings of the first row
and the first column are used as template for the settings of the newly created rows and columns.setLayoutPolicy(byte),
Constant Field Valuespublic static final byte LAYOUT_POLICY_FIXED_SIZE
PartitionGrid instance.
The algorithm generates a tabular layout with the number of rows and
columns as specified by the registered grid instance.
The settings of the respective RowDescriptors and ColumnDescriptors are considered.
Using this layout policy, it is possible to exactly define in which cell of the table
a certain node should be placed by mapping a specific PartitionCellId to a node.
PartitionCellId instances can be created using methods PartitionGrid.createCellId(int, int) and
PartitionGrid.createCellId(RowDescriptor, ColumnDescriptor). Multi-cells (see e.g.
PartitionGrid.createCellSpanId(int, int, int, int)) are not allowed. The node-cell mapping must be
defined in a DataProvider registered with the graph with key PartitionGrid.PARTITION_CELL_DPKEY.
Nodes without a specific mapping to a cell are inserted one after another in a row-wise manner
in the order defined by the specified getNodeComparator().
PartitionGrid.PARTITION_GRID_DPKEY.PartitionGrid instance must be large enough for all nodes to fit
into the grid. Otherwise, a WrongGraphStructure exception will be thrown.setLayoutPolicy(byte),
Constant Field Valuespublic static final byte LAYOUT_POLICY_FROM_SKETCH
Enabling this feature, the current layout of the input graph will be interpreted as a sketch for the layout algorithm. Nodes are assigned to the same row if there exists a horizontal line that crosses through both of their bounding boxes. Similarly, nodes are assigned to the same column if there exists a vertical line that crosses through both of their bounding boxes. Clearly, this strategy only works smoothly if the given input already resembles a rough table arrangement.
If the given layout does not offer any division of the nodes into column and rows or contains overlapping nodes, then the sketch is ambiguous and the algorithm will chose one valid variant.
PartitionGrid instance to get the computed location and the dimension
of the table after the layout run. To do so query the according value from the
RowDescriptors and ColumnDescriptors associated with the grid.PartitionGrid instance is registered that already contains rows
and/or columns, the number of rows/columns is ignored and,
furthermore, the list of rows will be cleared. However, the settings of the first row
and the first column are used as template for the settings of the newly created rows and columns.setLayoutPolicy(byte),
Constant Field Values| Constructor Detail |
|---|
public TabularLayouter()
| Method Detail |
|---|
public NodeLayoutDescriptor getDefaultNodeLayoutDescriptor()
NodeLayoutDescriptor instance used for all the nodes that do not have an individual
layout descriptor.
NodeLayoutDescriptor instanceNODE_LAYOUT_DESCRIPTOR_DPKEY,
setDefaultNodeLayoutDescriptor(NodeLayoutDescriptor)public void setDefaultNodeLayoutDescriptor(NodeLayoutDescriptor descriptor)
NodeLayoutDescriptor instance used for all the nodes that do not have an individual
layout descriptor.
NodeLayoutDescriptor. Descriptor instance with default settings.descriptor - the default NodeLayoutDescriptor instance
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException - if the specified descriptor is nullNODE_LAYOUT_DESCRIPTOR_DPKEYpublic byte getLayoutPolicy()
This policy is a crucial setting for the algorithm and should be chosen depending on the desired use case. Overview over the policies:
LAYOUT_POLICY_AUTO_SIZE: no PartitionGrid instance required. The size of the table
is chosen automatically and nodes are sorted using getNodeComparator().
LAYOUT_POLICY_FIXED_SIZE: requires a registered PartitionGrid instance that defines
the size of the tabular layout and, optionally, the mapping of nodes to specific cells.
LAYOUT_POLICY_FROM_SKETCH: no PartitionGrid instance required. The size of the table
and the positioning of the nodes is solely derived from the coordinates of the input graph (sketch).
setLayoutPolicy(byte)public void setLayoutPolicy(byte layoutPolicy)
This policy is a crucial setting for the algorithm and should be chosen depending on the desired use case. Overview over the policies:
LAYOUT_POLICY_AUTO_SIZE: no PartitionGrid instance required. The size of the table
is chosen automatically and nodes are sorted using getNodeComparator().
LAYOUT_POLICY_FIXED_SIZE: requires a registered PartitionGrid instance that defines
the size of the tabular layout and, optionally, the mapping of nodes to specific cells.
LAYOUT_POLICY_FROM_SKETCH: no PartitionGrid instance required. The size of the table
and the positioning of the nodes is solely derived from the coordinates of the input graph (sketch).
LAYOUT_POLICY_AUTO_SIZElayoutPolicy - one of the predefined layout policies
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException - if the given policy is unknownpublic boolean isNodeLabelConsiderationEnabled()
Internally, nodes are treated like they would have a size including their labels. Therefore, layout results may get significantly larger if this feature is enabled.
true if node labels are considered, false otherwisesetNodeLabelConsiderationEnabled(boolean)public void setNodeLabelConsiderationEnabled(boolean nodeLabelConsiderationEnabled)
Internally, nodes are treated like they would have a size including their labels. Therefore, layout results may get significantly larger if this feature is enabled.
public java.util.Comparator getNodeComparator()
Comparator that defines the order in which the free nodes are placed in the table.
The nodes are arranged in the table in a row-wise fashion using the order provided by this
Comparator, i.e., the first row is filled from left to right, then the second row is filled, again
from left to right etc.
Nodes that are mapped to specific PartitionCellId are considered to be fixed and are
not sorted using this Comparator. This only applies when using policy LAYOUT_POLICY_FIXED_SIZE.
Furthermore, if LAYOUT_POLICY_FROM_SKETCH is active, this property is ignored.
Comparator that defines the node order or null if the order should be
defined by the internal node indicessetNodeComparator(Comparator)public void setNodeComparator(java.util.Comparator comp)
Comparator that defines the order in which the free nodes are placed in the table.
The nodes are arranged in the table in a row-wise fashion using the order provided by this
Comparator, i.e., the first row is filled from left to right, then the second row is filled, again
from left to right etc.
Nodes that are mapped to specific PartitionCellId are considered to be fixed and are
not sorted using this Comparator. This only applies when using policy LAYOUT_POLICY_FIXED_SIZE.
Furthermore, if LAYOUT_POLICY_FROM_SKETCH is active, this property is ignored.
comp - the Comparator that defines the node order or null if the order should be
defined by the internal node indicespublic boolean canLayout(LayoutGraph graph)
canLayout in interface Layoutergraph - the input graph
true for all kinds of graphsLayouter.doLayout(LayoutGraph)public void doLayout(LayoutGraph graph)
doLayout in interface Layoutergraph - the input graphLayouter.canLayout(LayoutGraph)
|
© Copyright 2000-2025, yWorks GmbH. All rights reserved. |
||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | ||||||||
| SUMMARY: NESTED | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | ||||||||