 y.layout.AbstractLayoutStage
y.layout.AbstractLayoutStage
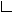 y.layout.router.ChannelEdgeRouter
y.layout.router.ChannelEdgeRouter
|
Search this API | ||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | ||||||||
| SUMMARY: NESTED | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | ||||||||
java.lang.Objecty.layout.AbstractLayoutStage
y.layout.router.ChannelEdgeRouter
public class ChannelEdgeRouter
This edge routing algorithm generates orthogonal routes for the edges of the graph.
Compared to the routing algorithms implemented by classes EdgeRouter
and OrthogonalEdgeRouter, this implementation is usually faster but supports
less constraints and, by default, may produce node-edge overlaps.
Edges are routed in an orthogonal fashion, i.e., edge paths consist only of vertical and horizontal segments.
During the routing process, the positions of the nodes are considered to be fixed and the routing algorithm will not modify their locations or their sizes in any way.
The edge routing algorithm can be applied wherever it is required to route the edges as orthogonal segments, while keeping the positions of the nodes in the diagram fixed. Some potential applications include electric circuit design, floor planning, UML class diagrams/inheritance diagrams and navigation maps.
Sample output of the orthogonal edge routing algorithm with default settings
This edge routing algorithm combines two strategic steps of edge routing and executes them one after the other. The first strategy is called path finder strategy and will route the edges, potentially with edge overlaps. The second strategy will then split overlapping edge segments inside their channels and distribute them according to the specific distribution strategy.
The default path finding strategy is OrthogonalPatternEdgeRouter. Alternatively, you can
use ChannelEdgeRouter.OrthogonalShortestPathPathFinder. The default edge distribution strategy is
OrthogonalSegmentDistributionStage.
This class itself has no special routing options except from specifying the path finding
and edge distribution strategy.
Most of the features like minimum element distances, grid spacing and path restrictions
have to be set on the used instances for the two routing steps.
For incremental edge routing, DataProvider key AFFECTED_EDGES has to be registered with the graph
to mark all edges that should be routed by the algorithm. The routes of the other edges remain unchanged.
If there is no such key registered, the algorithm routes all edges.
AFFECTED_EDGES to determine
the affected edges.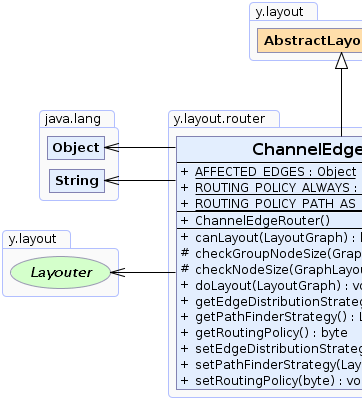 |
 |
| Nested Class Summary | |
|---|---|
static class |
ChannelEdgeRouter.OrthogonalShortestPathPathFinder
This routing algorithm is a special version of class OrthogonalEdgeRouter that can be used as a path
finding strategy for the ChannelEdgeRouter. |
| Field Summary | |
|---|---|
static java.lang.Object |
AFFECTED_EDGES
A DataProvider key for marking the edges that should be routed.
|
static byte |
ROUTING_POLICY_ALWAYS
A routing policy that indicates that a new route is calculated in any case. |
static byte |
ROUTING_POLICY_PATH_AS_NEEDED
A routing policy that indicates that based on the current path it is automatically determined whether an edge is routed, and if so, the edge gets a whole new path. |
| Fields inherited from interface y.layout.Layouter |
|---|
EDGE_ID_DPKEY, NODE_ID_DPKEY, NODE_TYPE_DPKEY, SELECTED_EDGES, SELECTED_NODES |
| Constructor Summary | |
|---|---|
ChannelEdgeRouter()
Creates a new ChannelEdgeRouter instance with default settings. |
|
| Method Summary | |
|---|---|
boolean |
canLayout(LayoutGraph graph)
Checks whether or not the given graph can be handled by this edge routing algorithm. |
protected void |
checkGroupNodeSize(GraphLayout layout,
java.lang.Object node)
Checks the given group node for zero or negative width/height. |
protected void |
checkNodeSize(GraphLayout layout,
java.lang.Object node)
Checks the given node for zero or negative width/height. |
void |
doLayout(LayoutGraph graph)
Performs the orthogonal routing of the edges of the input graph. |
Layouter |
getEdgeDistributionStrategy()
Returns the strategy for the edge distribution step. |
Layouter |
getPathFinderStrategy()
Returns the strategy for the path finding step. |
byte |
getRoutingPolicy()
Returns the routing policy indicating if the edges are unconditionally routed or if the existing routes determines whether a new path is necessary. |
void |
setEdgeDistributionStrategy(Layouter edgeDistributionStrategy)
Specifies the strategy for the edge distribution step. |
void |
setPathFinderStrategy(Layouter pathFinderStrategy)
Specifies the strategy for the path finding step. |
void |
setRoutingPolicy(byte routingPolicy)
Specifies the routing policy indicating if the edges are unconditionally routed or if the existing routes determines whether a new path is necessary. |
| Methods inherited from class y.layout.AbstractLayoutStage |
|---|
canLayoutCore, doLayoutCore, getCoreLayouter, setCoreLayouter |
| Methods inherited from class java.lang.Object |
|---|
clone, equals, finalize, getClass, hashCode, notify, notifyAll, toString, wait, wait, wait |
| Field Detail |
|---|
public static final java.lang.Object AFFECTED_EDGES
DataProvider key for marking the edges that should be routed.
If this key is not registered with the graph, the algorithm will route all edges.
public static final byte ROUTING_POLICY_ALWAYS
The existing path of an edge is ignored and the routing algorithm unconditionally generates a whole new path.
public static final byte ROUTING_POLICY_PATH_AS_NEEDED
The automatic selection examines the existing, given path of an edge. Based on various criteria it heuristically determines whether or not it needs to be routed. For example, intersections with other elements or a routing style violation are clear indicators. A further criterion is when the port constraints/candidates are not properly satisfied. Edges deemed to be 'good' are not changed.
This policy is convenient for cases where it is not clear which edges the algorithm should route. For example, after a user interaction (moving a node, inserting new elements etc.), routing of edges might become necessary but depending on the action it can not definitely be said which edges need to be corrected.
| Constructor Detail |
|---|
public ChannelEdgeRouter()
ChannelEdgeRouter instance with default settings.
| Method Detail |
|---|
public boolean canLayout(LayoutGraph graph)
true unless the user specifies a core layout algorithm
that cannot handle this graph or if the width/height of a node is zero.
graph - the input graph
true if the input graph can be handled by this edge routing algorithm, false
otherwiseLayouter.doLayout(LayoutGraph)public void doLayout(LayoutGraph graph)
graph - the input graphLayouter.canLayout(LayoutGraph)
protected void checkNodeSize(GraphLayout layout,
java.lang.Object node)
throws java.lang.IllegalArgumentException
This method is called before the invocation of the core layout algorithm
for each normal node of the input graph. It may be overridden in order to obtain a custom implementation
of node-size check or to remove it entirely.
layout - the GraphLayout instancenode - the node object
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException - if the width/height of the node object is zero or negativecheckGroupNodeSize(GraphLayout, Object),
canLayout(LayoutGraph),
doLayout(LayoutGraph)
protected void checkGroupNodeSize(GraphLayout layout,
java.lang.Object node)
throws java.lang.IllegalArgumentException
This method is called by doLayout(LayoutGraph) for each group node of the input graph.
It may be overridden in order to obtain a custom implementation of group-node-size check or to remove it entirely.
layout - the GraphLayout instancenode - the group node object
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException - if the width/height of the group node object is zero or negativecheckNodeSize(GraphLayout,Object)public void setPathFinderStrategy(Layouter pathFinderStrategy)
This step routes the edges and may produce edge overlaps which are later resolved in the
edge distribution step.
AFFECTED_EDGES to determine the
affected edges.OrthogonalPatternEdgeRouterpathFinderStrategy - the path finding strategy that should be setpublic void setEdgeDistributionStrategy(Layouter edgeDistributionStrategy)
This step distributes overlapping edge segments in their channel. The channel in which the segments can be distributed is defined by the surrounding graph elements.
AFFECTED_EDGES to determine the
affected edges.OrthogonalSegmentDistributionStageedgeDistributionStrategy - the distribution strategy to be setpublic Layouter getPathFinderStrategy()
This step routes the edges and may produce edge overlaps which are later resolved in the
edge distribution step.
AFFECTED_EDGES to determine the
affected edges.setPathFinderStrategy(Layouter)public Layouter getEdgeDistributionStrategy()
This step distributes overlapping edge segments in their channel. The channel in which the segments can be distributed is defined by the surrounding graph elements.
AFFECTED_EDGES to determine the
affected edges.setEdgeDistributionStrategy(Layouter)public byte getRoutingPolicy()
ROUTING_POLICY_ALWAYS and
ROUTING_POLICY_PATH_AS_NEEDED. Only routing specific segments as needed is not supported.setRoutingPolicy(byte)public void setRoutingPolicy(byte routingPolicy)
ROUTING_POLICY_ALWAYS and
ROUTING_POLICY_PATH_AS_NEEDED. Only routing specific segments as needed is not supported.ROUTING_POLICY_ALWAYS. The edges are routed, ignoring the existing sketch.routingPolicy - one of the two predefined routing policies
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException - if an unknown routing policy is given
|
© Copyright 2000-2025, yWorks GmbH. All rights reserved. |
||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | ||||||||
| SUMMARY: NESTED | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | ||||||||