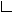 y.layout.hierarchic.incremental.RoutingStyle
y.layout.hierarchic.incremental.RoutingStyle
|
Search this API | ||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | ||||||||
| SUMMARY: NESTED | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | ||||||||
java.lang.Objecty.layout.hierarchic.incremental.RoutingStyle
public class RoutingStyle
This class is used by EdgeLayoutDescriptor to specify the routing style for different types of edges.
EdgeLayoutDescriptor.setRoutingStyle(RoutingStyle),
EdgeData.getType()
| Field Summary | |
|---|---|
static byte |
EDGE_STYLE_CURVED
A routing style constant specifying that the edges should be curved. |
static byte |
EDGE_STYLE_OCTILINEAR
A routing style constant specifying that the edges should be octilinear. |
static byte |
EDGE_STYLE_ORTHOGONAL
A routing style constant specifying that the edges should be orthogonal. |
static byte |
EDGE_STYLE_POLYLINE
A routing style constant specifying that the edges should be polyline. |
| Constructor Summary | |
|---|---|
RoutingStyle(byte routingStyle)
Creates a new RoutingStyle instance with the given routing style for each edge. |
|
RoutingStyle(byte routingStyle,
boolean controlPointCreation)
Creates a new RoutingStyle instance with the given routing style for each edge and also specifying
whether or not the resulting path should consist of cubic bezier control points. |
|
| Method Summary | |
|---|---|
byte |
getBackloopRoutingStyle()
Returns the routing style for back-loop edges. |
double |
getCurveUTurnSymmetry()
Returns how symmetric u-turn parts of curved routes should preferably be. |
byte |
getDefaultEdgeRoutingStyle()
Returns the default routing style for edges that have no individual routing style. |
byte |
getEdgeGroupRoutingStyle()
Returns the routing style for grouped edges at the common segments. |
byte |
getSameLayerEdgeRoutingStyle()
Returns the routing style for same-layer edges. |
byte |
getSelfloopRoutingStyle()
Returns the routing style for self-loops. |
byte |
getSourceCurveConnectionStyle()
Returns the style which determines how curved edge paths connect at the source side of the edge. |
byte |
getTargetCurveConnectionStyle()
Returns the style which determines how curved edge paths connect at the target side of the edge. |
boolean |
isControlPointCreationEnabled()
Returns whether or not the points of the resulting edge path represent cubic bezier control points. |
boolean |
isCurveShortcutsAllowed()
Returns whether or not curved edges may shortcut and introduce
additional edge crossings to make curves more direct and smoother. |
void |
setBackloopRoutingStyle(byte backloopRoutingStyle)
Specifies the routing style for back-loop edges. |
void |
setControlPointCreationEnabled(boolean controlPointCreation)
Specifies whether or not the points of the resulting edge path represent cubic bezier control points. |
void |
setCurveShortcutsAllowed(boolean curveShortcutsAllowed)
Specifies whether or not curved edges may shortcut and introduce
additional edge crossings to make curves more direct and smoother. |
void |
setCurveUTurnSymmetry(double curveUTurnSymmetry)
Specifies how symmetric u-turn parts of curved routes should preferably be. |
void |
setDefaultEdgeRoutingStyle(byte defaultEdgeRoutingStyle)
Specifies the default routing style for edges that have no individual routing style. |
void |
setEdgeGroupRoutingStyle(byte edgeGroupRoutingStyle)
Specifies the routing style for grouped edges at the common segments. |
void |
setSameLayerEdgeRoutingStyle(byte sameLayerEdgeRoutingStyle)
Specifies the routing style for same-layer edges. |
void |
setSelfloopRoutingStyle(byte selfloopRoutingStyle)
Specifies the routing style for self-loops. |
void |
setSourceCurveConnectionStyle(byte curveConnectionStyle)
Specifies the style which determines how curved edge paths connect at the source side of the edge. |
void |
setTargetCurveConnectionStyle(byte curveConnectionStyle)
Specifies the style which determines how curved edge paths connect at the target side of the edge. |
| Methods inherited from class java.lang.Object |
|---|
clone, equals, finalize, getClass, hashCode, notify, notifyAll, toString, wait, wait, wait |
| Field Detail |
|---|
public static final byte EDGE_STYLE_ORTHOGONAL
public static final byte EDGE_STYLE_OCTILINEAR
-1 and 1.
public static final byte EDGE_STYLE_POLYLINE
public static final byte EDGE_STYLE_CURVED
Curved edges are constructed using cubic bezier splines. As for other routing styles, overlaps with other
elements are avoided. If there is very little space for a smooth curve, it can happen that the resulting
path is polyline or almost polyline with little curving. To reserve more space for curved edges,
one can increase values of settings that influence the distances between graph elements, e.g.,
EdgeLayoutDescriptor.getMinimumDistance().
When integrated edge labeling is enabled, for edge labels a straight, non-curved segment where the label
is placed will be inserted. All the settings of the PreferredPlacementDescriptor are supported.
Similarly, for the minimum first segment length
and the minimum last segment length, a straight
edge segment is created to fulfill the constraints.
setControlPointCreationEnabled(boolean) Routing style curved |
| Constructor Detail |
|---|
public RoutingStyle(byte routingStyle)
RoutingStyle instance with the given routing style for each edge.
routingStyle - one of the predefined routing styles
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException - if an unknown routing style is given
public RoutingStyle(byte routingStyle,
boolean controlPointCreation)
RoutingStyle instance with the given routing style for each edge and also specifying
whether or not the resulting path should consist of cubic bezier control points.
routingStyle - one of the predefined routing stylescontrolPointCreation - true if the resulting path should consist of cubic bezier
control points, false otherwise
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException - if an unknown routing style is given| Method Detail |
|---|
public byte getBackloopRoutingStyle()
This style is used for routing U-turns of common edges (i.e., edges that are neither self-loops nor same-layer
edges). A U-turn is a non-monotonic part of the edge route that is required for reversed edges if option
IncrementalHierarchicLayouter.setBackloopRoutingEnabled(boolean) is enabled
or in some other scenarios with port constraints/candidates.
setBackloopRoutingStyle(byte)public void setBackloopRoutingStyle(byte backloopRoutingStyle)
This style is used for routing U-turns of common edges (i.e., edges that are neither self-loops nor same-layer
edges). A U-turn is a non-monotonic part of the edge route that is required for reversed edges if option
IncrementalHierarchicLayouter.setBackloopRoutingEnabled(boolean) is enabled
or in some other scenarios with port constraints/candidates.
backloopRoutingStyle - one of the predefined routing styles
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException - if an unknown routing style is givenpublic byte getEdgeGroupRoutingStyle()
More precisely, grouped edges are routed in a bus-style fashion (i.e., the paths of the edges will share a common edge segment) and this option allows to specify the routing style at the bus.
setEdgeGroupRoutingStyle(byte)public void setEdgeGroupRoutingStyle(byte edgeGroupRoutingStyle)
More precisely, grouped edges are routed in a bus-style fashion (i.e., the paths of the edges will share a common edge segment) and this option allows to specify the routing style at the bus.
edgeGroupRoutingStyle - one of the predefined routing styles
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException - if an unknown routing style is givenpublic byte getDefaultEdgeRoutingStyle()
public void setDefaultEdgeRoutingStyle(byte defaultEdgeRoutingStyle)
defaultEdgeRoutingStyle - one of the predefined routing styles
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException - if an unknown routing style is givenpublic byte getSameLayerEdgeRoutingStyle()
A same-layer edge is an edge whose source/target are assigned to the same layer.
setSameLayerEdgeRoutingStyle(byte)public void setSameLayerEdgeRoutingStyle(byte sameLayerEdgeRoutingStyle)
A same-layer edge is an edge whose source/target are assigned to the same layer.
sameLayerEdgeRoutingStyle - one of the predefined routing styles
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException - if an unknown routing style is givenpublic byte getSelfloopRoutingStyle()
setSelfloopRoutingStyle(byte)public void setSelfloopRoutingStyle(byte selfloopRoutingStyle)
selfloopRoutingStyle - one of the predefined routing styles
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException - if an unknown routing style is givenpublic byte getSourceCurveConnectionStyle()
CurveConnectionStyle.ORGANIC, the source port may end up not being on the
side of the node pointing in the main layout direction anymore. For example, the port may be moved to the
left or right side of the node for the default top-to-bottom layout orientation.curved edge
routing style.setTargetCurveConnectionStyle(byte),
setSourceCurveConnectionStyle(byte)public void setSourceCurveConnectionStyle(byte curveConnectionStyle)
CurveConnectionStyle.ORGANIC, the source port may end up not being on the
side of the node pointing in the main layout direction anymore. For example, the port may be moved to the
left or right side of the node for the default top-to-bottom layout orientation.curved edge
routing style.CurveConnectionStyle.KEEP_PORT. The hierarchic source port and the first segment is kept.curveConnectionStyle - one of the predefined curve connection styles
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException - if an unknown connection style is givensetTargetCurveConnectionStyle(byte) Curved edges with the source and target ports kept as they are in a hierarchic layout |  Organic-like curve connections at source and target side |
public byte getTargetCurveConnectionStyle()
CurveConnectionStyle.ORGANIC, the target port may end up not being on the
side of the node pointing against the main layout direction anymore. For example, the port may be moved to the
left or right side of the node for the default top-to-bottom layout orientation.curved edge
routing style.setSourceCurveConnectionStyle(byte),
setTargetCurveConnectionStyle(byte)public void setTargetCurveConnectionStyle(byte curveConnectionStyle)
CurveConnectionStyle.ORGANIC, the target port may end up not being on the
side of the node pointing against the main layout direction anymore. For example, the port may be moved to the
left or right side of the node for the default top-to-bottom layout orientation.curved edge
routing style.CurveConnectionStyle.KEEP_PORT. The hierarchic target port and the last segment is kept.curveConnectionStyle - one of the predefined curve connection styles
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException - if an unknown connection style is givensetSourceCurveConnectionStyle(byte) Curved edges with the source and target ports kept as they are in a hierarchic layout |  Organic-like curve connections at source and target side |
public boolean isCurveShortcutsAllowed()
curved edges may shortcut and introduce
additional edge crossings to make curves more direct and smoother.
In relation to nodes, labels and other edges, the curved and non-curved edges take the same route, for example, both might cross a certain other edge or pass a certain node on its left side. If this property is disabled (default), the curved edges adhere to this.
If enabled, however, curved edges may shortcut and cross additional edges. This can yield to a direct and possibly smoother curved route. Still, intersections with nodes, node labels and edge labels are not allowed.
symmetric u-turn curves are preferred, enabling this property
may be beneficial. For example, creating a perfectly symmetric u-turn curve may require to cross an additional edge.curved edge routing style.
It is not possible to precisely predict the impact of this setting for the general case.
Usually, the effect of this property can mainly be observed for long edges close to the exterior of large graphs.true, if curved edges may shortcut in favor of more direct curves,
false, otherwiseEDGE_STYLE_CURVED,
setCurveShortcutsAllowed(boolean)public void setCurveShortcutsAllowed(boolean curveShortcutsAllowed)
curved edges may shortcut and introduce
additional edge crossings to make curves more direct and smoother.
In relation to nodes, labels and other edges, the curved and non-curved edges take the same route, for example, both might cross a certain other edge or pass a certain node on its left side. If this property is disabled (default), the curved edges adhere to this.
If enabled, however, curved edges may shortcut and cross additional edges. This can yield to a direct and possibly smoother curved route. Still, intersections with nodes, node labels and edge labels are not allowed.
symmetric u-turn curves are preferred, enabling this property
may be beneficial. For example, creating a perfectly symmetric u-turn curve may require to cross an additional edge.curved edge routing style.
It is not possible to precisely predict the impact of this setting for the general case.
Usually, the effect of this property can mainly be observed for long edges close to the exterior of large graphs.curveShortcutsAllowed - true, if curved edges may shortcut in favor
of more direct curves, false, otherwiseEDGE_STYLE_CURVED Curve shortcuts are disabled |  Curve shortcuts are enabled |
public double getCurveUTurnSymmetry()
curved routes should preferably be.
If this property is greater than zero, the algorithm tries to achieve a more symmetric path for
180-degree turns (u-turns) by specifically handling them. Symmetric turns likely require more space compared
to more direct variants.
The value of this property must be within interval [0,1], where a higher value indicates
more emphasis on symmetry and lower values that symmetry is not important.
This setting influences the symmetry of a single curved route and does not affect symmetry of multiple curves in relation to each other.
0 might be perceived as being greater than the difference
between other values. The reason is that with 0, u-turns are not handled specifically at all.curved edge routing style.[0,1], where a higher value means that symmetric turns are preferredEDGE_STYLE_CURVED,
setCurveUTurnSymmetry(double)public void setCurveUTurnSymmetry(double curveUTurnSymmetry)
curved routes should preferably be.
If this property is greater than zero, the algorithm tries to achieve a more symmetric path for
180-degree turns (u-turns) by specifically handling them. Symmetric turns likely require more space compared
to more direct variants.
The value of this property must be within interval [0,1], where a higher value indicates
more emphasis on symmetry and lower values that symmetry is not important.
This setting influences the symmetry of a single curved route and does not affect symmetry of multiple curves in relation to each other.
0 might be perceived as being greater than the difference
between other values. The reason is that with 0, u-turns are not handled specifically at all.curved edge routing style.curveUTurnSymmetry - the symmetry preference for u-turns of curved edges within interval
[0,1], where a higher value means that symmetric turns are preferred
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException - if the given symmetry value is negative or larger than oneEDGE_STYLE_CURVED 0.0 | 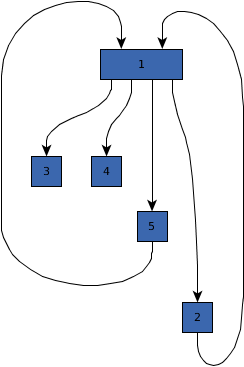 0.7 | 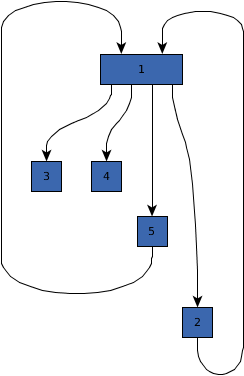 1.0 |
public boolean isControlPointCreationEnabled()
true if the bends are interpreted as cubic bezier control points, false otherwisesetControlPointCreationEnabled(boolean)public void setControlPointCreationEnabled(boolean controlPointCreation)
controlPointCreation - true if the points of the edge path should represent cubic
bezier control points, false otherwise
|
© Copyright 2000-2025, yWorks GmbH. All rights reserved. |
||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | ||||||||
| SUMMARY: NESTED | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | ||||||||