 y.layout.AbstractLayoutStage
y.layout.AbstractLayoutStage
 y.layout.tree.TreeReductionStage
y.layout.tree.TreeReductionStage
|
Search this API | ||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | ||||||||
| SUMMARY: NESTED | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | ||||||||
java.lang.Objecty.layout.AbstractLayoutStage
y.layout.tree.TreeReductionStage
public class TreeReductionStage
The TreeReductionStage temporarily reduces general graphs to trees.
This stage prepares a non-tree graph such that it can be processed by a tree layout algorithm.
Typical usage:
TreeLayouter tl = new TreeLayouter(); TreeReductionStage trs = new TreeReductionStage(); trs.setNonTreeEdgeRouter(new OrganicEdgeRouter()); trs.setNonTreeEdgeSelectionKey(OrganicEdgeRouter.ROUTE_EDGE_DPKEY); tl.prependStage(trs); new BufferedLayouter(tl).doLayout(graph); tl.removeStage(trs);
This LayoutStage works in three steps:
core layout algorithm which supports tree graph handling
The routing of the temporarily hidden non-tree edges can be customized by specifying an
edge routing algorithm for those edges. Similarly, the placement of edge labels
of non-tree edges can be delegated to a custom edge labeling algorithm.
As default, both custom algorithms are not specified and, thus, non-tree edges are not routed and edge labels not
placed.
This stage is also able to handle multi-parent structures, i.e., structures of multiple nodes
that share the same predecessors as well as the same successors. More precisely, if the specified
core layout algorithm supports multi-parent structures
(see GenericTreeLayouter.setMultiParentAllowed(boolean)) and option setMultiParentAllowed(boolean)
is enabled, this stage does not hide such structures, i.e., the multi-parent structures are passed to the
core layout algorithm.
Non-tree edges can also be bundled together such that their common parts are to some degree merged into a bundled
part. The edge bundling can be specified by means of method getEdgeBundling().
DataAcceptor can be registered with the specified
non-tree selection key. The algorithm will mark the non-tree edges.TreeLayouter may throw a
WrongGraphStructure-Exception. Such exceptions can be prevented by temporarily removing
those edges.| Field Summary | |
|---|---|
static java.lang.Object |
NON_TREE_EDGES_DPKEY
A DataProvider key for explicitly marking (some) edges that should not be considered for the tree
|
| Fields inherited from interface y.layout.Layouter |
|---|
EDGE_ID_DPKEY, NODE_ID_DPKEY, NODE_TYPE_DPKEY, SELECTED_EDGES, SELECTED_NODES |
| Constructor Summary | |
|---|---|
TreeReductionStage()
Creates a new TreeReductionStage instance with default settings. |
|
TreeReductionStage(Layouter core)
Creates a new TreeReductionStage instance with the given core layout algorithm and default settings. |
|
| Method Summary | |
|---|---|
boolean |
canLayout(LayoutGraph graph)
Accepts all general graphs without exception. |
Layouter |
createStraightlineRouter()
Creates a routing algorithm that routes edges as a single straight segment. |
void |
doLayout(LayoutGraph graph)
Determines a spanning tree of the graph and passes it to the core layout algorithm. |
EdgeBundling |
getEdgeBundling()
Returns the EdgeBundling instance that defines the settings of the edge bundling feature. |
Layouter |
getNonTreeEdgeLabelingAlgorithm()
Returns the labeling algorithm that is applied to all edge labels that belong to non-tree edges. |
java.lang.Object |
getNonTreeEdgeLabelSelectionKey()
Returns the key to register a DataProvider that is used by the
non-tree edge labeling algorithm to determine which edge labels
it should place. |
Layouter |
getNonTreeEdgeRouter()
Returns the edge routing algorithm that is applied to all non-tree edges. |
java.lang.Object |
getNonTreeEdgeSelectionKey()
Returns the key to register a DataProvider that will be used by the
non-tree edge routing algorithm to determine the edges that need to be routed. |
boolean |
isMultiParentAllowed()
Returns whether or not multi-parent structures (structures of multiple nodes that share the same predecessors as well as the same successors) are allowed. |
protected void |
routeNonTreeEdges(LayoutGraph graph,
EdgeMap nonTreeEdgeMap)
Routes all edges that do not belong to the chosen spanning tree. |
void |
setMultiParentAllowed(boolean multiParentAllowed)
Specifies whether or not multi-parent structures (structures of multiple nodes that share the same predecessors as well as the same successors) are allowed. |
void |
setNonTreeEdgeLabelingAlgorithm(Layouter nonTreeEdgeLabelingAlgorithm)
Specifies the labeling algorithm that is applied to all edge labels that belong to non-tree edges. |
void |
setNonTreeEdgeLabelSelectionKey(java.lang.Object nonTreeEdgeLabelSelectionKey)
Specifies the key to register a DataProvider that is used by the
non-tree edge labeling algorithm to determine which edge labels
it should place. |
void |
setNonTreeEdgeRouter(Layouter nonTreeEdgeRouter)
Specifies the edge routing algorithm that is applied to all non-tree edges. |
void |
setNonTreeEdgeSelectionKey(java.lang.Object nonTreeEdgeSelectionKey)
Specifies the key to register a DataProvider that will be used by the
non-tree edge routing algorithm to determine the edges that need to be routed. |
| Methods inherited from class y.layout.AbstractLayoutStage |
|---|
canLayoutCore, doLayoutCore, getCoreLayouter, setCoreLayouter |
| Methods inherited from class java.lang.Object |
|---|
clone, equals, finalize, getClass, hashCode, notify, notifyAll, toString, wait, wait, wait |
| Field Detail |
|---|
public static final java.lang.Object NON_TREE_EDGES_DPKEY
DataProvider key for explicitly marking (some) edges that should not be considered for the tree
getNonTreeEdgeRouter()| Constructor Detail |
|---|
public TreeReductionStage()
TreeReductionStage instance with default settings.
public TreeReductionStage(Layouter core)
TreeReductionStage instance with the given core layout algorithm and default settings.
core - the core layout algorithm| Method Detail |
|---|
public boolean canLayout(LayoutGraph graph)
graph - the input graph
true for all input graphsLayouter.doLayout(LayoutGraph)public void doLayout(LayoutGraph graph)
core layout algorithm.
This LayoutStage reduces the graph to a tree. Then, it applies the core layout algorithm to that tree.
After it gets the result, it reinserts the non-tree edges and routes them.
graph - the input graphLayouter.canLayout(LayoutGraph)
protected void routeNonTreeEdges(LayoutGraph graph,
EdgeMap nonTreeEdgeMap)
This method is called by doLayout(LayoutGraph) after the tree was arranged by the
core layout algorithm. It may be overridden to apply custom edge routes.
non-tree edge routing algorithm
was specified (i.e. if it is null).graph - the graph containing tree and non-tree edgesnonTreeEdgeMap - the EdgeMap that marks all non-tree edges in the graphpublic boolean isMultiParentAllowed()
More precisely, if this option is enabled and the specified core layout algorithm can
handle multi-parent structures (see GenericTreeLayouter.setMultiParentAllowed(boolean)),
this stage does not hide such structures, but the multi-parent structures are passed on to the
AbstractLayoutStage.getCoreLayouter() core layout algorithm}.
true if multi-parent structures are allowed, false otherwisesetMultiParentAllowed(boolean)public void setMultiParentAllowed(boolean multiParentAllowed)
More precisely, if this option is enabled and the specified core layout algorithm can
handle multi-parent structures (see GenericTreeLayouter.setMultiParentAllowed(boolean)),
this stage does not hide such structures, but the multi-parent structures are passed on to the
AbstractLayoutStage.getCoreLayouter() core layout algorithm}.
multiParentAllowed - true if multi-parent structures should be allowed, false otherwise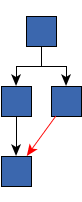 false - the multi-parent structure was reduced to a tree, a non-tree edge is marked | 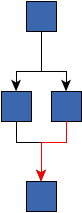 true - the multi-parent structure was not reduced and arranged using an appropriate style |
public Layouter getNonTreeEdgeRouter()
edge selection key is specified
and the router's scope is reduced to the selected edges.setNonTreeEdgeRouter(Layouter),
setNonTreeEdgeSelectionKey(Object)public void setNonTreeEdgeRouter(Layouter nonTreeEdgeRouter)
edge selection key is specified
and the router's scope is reduced to the selected edges.nonTreeEdgeRouter - the edge routing algorithm used for non-tree edgessetNonTreeEdgeSelectionKey(Object)public java.lang.Object getNonTreeEdgeSelectionKey()
DataProvider that will be used by the
non-tree edge routing algorithm to determine the edges that need to be routed.
DataAcceptor registered with this key, the stage uses it to mark the
non-tree edges. This way it can be determined which edges the layout treated as tree and which as non-tree edges.DataProvider keysetNonTreeEdgeSelectionKey(Object),
setNonTreeEdgeRouter(Layouter)public void setNonTreeEdgeSelectionKey(java.lang.Object nonTreeEdgeSelectionKey)
DataProvider that will be used by the
non-tree edge routing algorithm to determine the edges that need to be routed.
DataAcceptor registered with this key, the stage uses it to mark the
non-tree edges. This way it can be determined which edges the layout treated as tree and which as non-tree edges.DataProvider key specified.nonTreeEdgeSelectionKey - the DataProvider keysetNonTreeEdgeRouter(Layouter)public Layouter getNonTreeEdgeLabelingAlgorithm()
It is required that a suitable edge label selection key
is set. Otherwise, the edge labeling algorithm might also place labels of tree edges.
SALabeling. Specify the
edge label selection key as value of property
AbstractLabelingAlgorithm.setSelection(Object) and remember to enable
AbstractLabelingAlgorithm.setPlaceEdgeLabels(boolean).setNonTreeEdgeLabelSelectionKey(Object),
setNonTreeEdgeLabelingAlgorithm(Layouter)public void setNonTreeEdgeLabelingAlgorithm(Layouter nonTreeEdgeLabelingAlgorithm)
It is required that a suitable edge label selection key
is set. Otherwise, the edge labeling algorithm might also place labels of tree edges.
SALabeling. Specify the
edge label selection key as value of property
AbstractLabelingAlgorithm.setSelection(Object) and remember to enable
AbstractLabelingAlgorithm.setPlaceEdgeLabels(boolean).nonTreeEdgeLabelingAlgorithm - the labeling algorithm used for edge labels of non-tree edgessetNonTreeEdgeLabelSelectionKey(Object)public java.lang.Object getNonTreeEdgeLabelSelectionKey()
DataProvider that is used by the
non-tree edge labeling algorithm to determine which edge labels
it should place.
DataProvider with this key will be registered with the graph. It will
mark all EdgeLabelLayouts that belong to non-tree edges. The specified non-tree edge labeling
algorithm needs to obey this selection. If using SALabeling as labeling
algorithm, set this key as value of property AbstractLabelingAlgorithm.setSelection(Object).non-tree edge labeling algorithm but no
edge label selection key, then the labeling algorithm might place all labels, including those that
belong to actual tree edges.DataProvider keysetNonTreeEdgeLabelSelectionKey(Object),
setNonTreeEdgeLabelingAlgorithm(Layouter)public void setNonTreeEdgeLabelSelectionKey(java.lang.Object nonTreeEdgeLabelSelectionKey)
DataProvider that is used by the
non-tree edge labeling algorithm to determine which edge labels
it should place.
DataProvider with this key will be registered with the graph. It will
mark all EdgeLabelLayouts that belong to non-tree edges. The specified non-tree edge labeling
algorithm needs to obey this selection. If using SALabeling as labeling
algorithm, set this key as value of property AbstractLabelingAlgorithm.setSelection(Object).non-tree edge labeling algorithm but no
edge label selection key, then the labeling algorithm might place all labels, including those that
belong to actual tree edges.DataProvider key specified.nonTreeEdgeLabelSelectionKey - the non-tree edge label selection DataProvider keysetNonTreeEdgeLabelingAlgorithm(Layouter)public Layouter createStraightlineRouter()
The created instance can be used for routing non-tree edges.
setNonTreeEdgeRouter(Layouter)public EdgeBundling getEdgeBundling()
EdgeBundling instance that defines the settings of the edge bundling feature.
The specified EdgeBundling defines global bundling properties. Settings for individual
edges can be defined by assigning an EdgeBundleDescriptor to an edge using a DataProvider
registered with key EdgeBundling.EDGE_BUNDLE_DESCRIPTOR_DPKEY. To enable bundling for all non-tree edges,
set a default bundle descriptor which has
bundling enabled.
If the graph contains self-loops that belong to the set of non-tree edges, the stage will invoke the router defined for the non-tree edges in order to route them. In the case where this is not desired, the user has to hide them from the stage and route them afterwards as desired.
TreeReductionStage should be combined
with a layout algorithm that produces planar layouts of the underlying tree (i.e., no edges of the tree cross each
other) as BalloonLayouter or GenericTreeLayouter.non-tree layouter is not applied to bundled edges.bundling is enabled and if the graph does not contain multi-parent structures.EdgeBundling instance defining the edge bundling setup
|
© Copyright 2000-2025, yWorks GmbH. All rights reserved. |
||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | ||||||||
| SUMMARY: NESTED | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | ||||||||