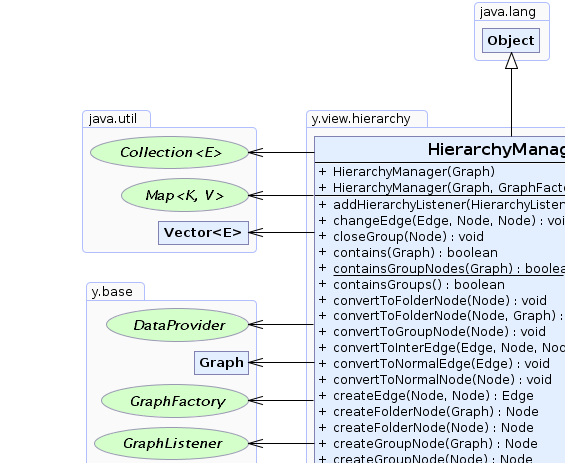
 y.view.hierarchy.HierarchyManager
y.view.hierarchy.HierarchyManager
|
Search this API | ||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | ||||||||
| SUMMARY: NESTED | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | ||||||||
java.lang.Objecty.view.hierarchy.HierarchyManager
public class HierarchyManager
This class manages a hierarchy of grouped nodes and nested graphs. A graph hierarchy always contains a top-level graph called the root graph. Each graph within the hierarchy can have an arbitrary number of nodes. These nodes can either be normal nodes, group nodes or so-called folder nodes. Folder nodes serve as proxy elements to access graphs in a lower hierarchy level. The graph that is accessible from a folder node is called the inner graph of that node. A folder node is also called anchor node, since it serves to attach an inner graph to a hierarchically higher graph. The hierarchically higher graph is called the parent graph of the inner graph.
Like a folder node, a group node can also contain other nodes that conceptually belong to a lower hierarchy level. Unlike a folder node, the child nodes of a group node belong to the same graph as the group node itself.
A hierarchy manager provides means to create new group and folder nodes within and/or remove existing group and folder nodes from a graph. Additionally, it provides means to move parts of a graph a level up or down in the hierarchy. Moreover, it provides means to group and ungroup nodes.
When moving parts of a graph to another hierarchy level, it is possible that the end points of edges come to lie in different graphs. The hierarchy manager will automatically redirect such edges in a clever and consistent way. An edge will always be part of the graph that is the hierarchically highest common ancestor of the graphs that contain the original source and target nodes of the edge. In case the original end point of the edge is not in the same graph, then the folder node hosting this end point will be chosen as local end point of that edge. Such a redirected edge is called an inter-edge, since it actually connects nodes in different graphs. The original end points of an inter-edge are called real node and real target.
A hierarchy manager listens for graph structure changes in the root graph (and
in any inner graphs created for folder nodes) in order to keep the model that
it maintains for the entire hierarchic structure consistent.
Vice versa, it fires high-level events that signal the change of the
hierarchic structure and the change of the node elements within the hierarchy.
Clients interested in this information must implement the HierarchyListener
interface and register to the hierarchy manager. Listeners will be informed by receiving
messages of type HierarchyEvent whenever the hierarchy changes.
Note that hierarchy events of type HierarchyEvent.NODE_CHANGED will not
be fired by the HierarchyManager itself since it does not know enough about
specific nodes. In order to receive NODE_CHANGED hierarchy events it is necessary
to add a GraphListener, or Graph2DListener to the root
graph of the hierarchy that translates the incoming events into
HierarchyEvents.
Class DefaultNodeChangePropagator, for example, serves this purpose.
The hierarchy manager is also responsible for creating new nodes and graphs
when the hierarchy grows. A hierarchy manager uses an aggregated factory of type
GraphFactory to create these elements. Clients can provide their own
factories to customize graph object creation.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Nested Class Summary | |
|---|---|
static interface |
HierarchyManager.InterEdgeData
Specifies the general contract for storing and retrieving additional data for inter-edges. |
static interface |
HierarchyManager.NodeVisitor
Callback interface that allows to perform some action when nodes within the hierarchy get visited in a certain order. |
| Constructor Summary | |
|---|---|
HierarchyManager(Graph rootGraph)
Creates a new hierarchy manager that initially manages a flat graph hierarchy whose root graph will be the given graph. |
|
HierarchyManager(Graph root,
GraphFactory factory)
Creates a new hierarchy manager that initially manages a flat graph hierarchy whose root graph will be the given graph. |
|
| Method Summary | |
|---|---|
void |
addHierarchyListener(HierarchyListener listener)
Adds a HierarchyListener to this HierarchyManager; |
void |
changeEdge(Edge e,
Node src,
Node tgt)
Changes the specified edge's end points. |
void |
closeGroup(Node groupNode)
Convenience method that performs all necessary steps to convert a group node to a folder node. |
boolean |
contains(Graph graph)
Returns whether or not the given graph is part of this graph hierarchy |
static boolean |
containsGroupNodes(Graph graph)
Whether or not the given graph contains any group nodes. |
boolean |
containsGroups()
Queries the hierarchy if it contains any group nodes. |
void |
convertToFolderNode(Node v)
Converts a group node or a normal node to a folder node. |
void |
convertToFolderNode(Node v,
Graph innerGraph)
Converts a group node or a normal node to a folder node. |
void |
convertToGroupNode(Node v)
Converts a folder node or a normal node to a group node. |
void |
convertToInterEdge(Edge e,
Node realSource,
Node realTarget)
Converts a normal edge to an inter-edge. |
void |
convertToNormalEdge(Edge e)
Converts an inter-edge to a normal edge. |
void |
convertToNormalNode(Node v)
Converts a group or folder node to a normal node. |
Edge |
createEdge(Node v,
Node w)
Convenience method that creates an edge in a nested graph hierarchy. |
Node |
createFolderNode(Graph parentGraph)
Similar to createFolderNode(Node). |
Node |
createFolderNode(Node parent)
Returns a newly created folder node that will be created as a child node of the given folder or group node. |
Node |
createGroupNode(Graph graph)
Similar to createGroupNode(Node). |
Node |
createGroupNode(Node parent)
Returns a newly created group node that will be created as a child node of the given group or folder node. |
void |
dispose()
Disposes this HierarchyManager instance. |
protected void |
fireHierarchyEvent(HierarchyEvent e)
Propagates the given hierarchy event to all registered hierarchy listeners. |
void |
foldSubgraph(NodeList subNodes,
Node folderNode)
Moves part of a graph into a folder node. |
Node |
getAnchorNode(Graph graph)
Returns the anchor node of the given graph. |
NodeCursor |
getChildren(Node node)
Returns all direct child nodes of a group or folder node. |
NodeList |
getFolderNodes(Graph rootGraph,
boolean recursive)
Returns all folder nodes that are either contained in given graph or contained in the given graph or one of its graph descendants. |
java.lang.Object[] |
getFolderPath(java.lang.Object item)
Returns the hierarchy of folder nodes that lie above the given item within this hierarchy. |
GraphFactory |
getGraphFactory()
Returns the registered graph factory of this hierarchy manager. |
DataProvider |
getGroupNodeDataProvider()
Returns a data provider the provides boolean values for each node indicating whether or not the given node is a group node. |
java.util.Iterator |
getHierarchyListeners()
Returns an iterator that grants access to all registered HierarchyListeners. |
Graph |
getInnerGraph(Node folderNode)
Returns the inner graph accessible from the given folder node. |
static HierarchyManager |
getInstance(Graph graph)
This static method returns the single hierarchy manager instance that is responsible for managing the given graph. |
InterEdgeConfigurator |
getInterEdgeConfigurator()
Returns the InterEdgeConfigurator used by this class. |
HierarchyManager.InterEdgeData |
getInterEdgeData(Edge e)
Returns a data object for storing and retrieving additional data associated to the specified inter-edge. |
int |
getLocalGroupDepth(Node node)
Returns the hierarchy level of the given node within its graph. |
Graph |
getNearestCommonAncestor(Graph g1,
Graph g2)
Finds the graph that is the nearest common ancestor of two graphs in the hierarchy. |
Node |
getNearestCommonAncestor(NodeList subNodes)
Finds the group or folder node that is the nearest common ancestor of all given nodes. |
DataProvider |
getNodeIdDataProvider()
Returns a data provider the provides a unique ID for each node within the hierarchy. |
Graph |
getParentGraph(Graph graph)
Returns the parent graph of the given graph within this hierarchy. |
Node |
getParentNode(Node node)
Returns the parent node of the given node. |
DataProvider |
getParentNodeIdDataProvider()
Returns a data provider the provides the parent ID for each node within the hierarchy. |
Node |
getRealSource(Edge e)
Returns the real source node associated with the given inter-edge. |
Node |
getRealTarget(Edge e)
Returns the real target node associated with the given inter-edge. |
Node |
getRepresentative(Node v,
Graph inGraph)
Convenience method that returns the Node representing a Node
in another Graph if the node lies in that graph is an ancestor of the node. |
Graph |
getRootGraph()
Returns the root graph of this hierarchy. |
java.lang.Object[] |
getTreePath(java.lang.Object item)
Returns the hierarchy of group and folder nodes that lie above the given item within this hierarchy. |
java.lang.Object[] |
getTreePath(java.lang.Object item,
boolean includeItem)
Like getTreePath(Object) with the additional option to
include the given item as the last element of the path. |
void |
groupSubgraph(NodeList subNodes,
Node groupNode)
Assigns the given nodes to the given group node. |
boolean |
isAncestor(Node presumedAncestor,
Node node)
Queries the hierarchy if a given node is an ancestor of another node in the hierarchy. |
boolean |
isFolderNode(Node v)
Returns whether or not the given node is a folder node. |
boolean |
isGroupNode(Node v)
Returns whether or not the given node is a group node. |
boolean |
isInterEdge(Edge e)
Returns whether or not the given edge is an inter-edge. |
boolean |
isNormalNode(Node v)
Returns whether or not the given node is a normal node, i.e., neither group nor folder node. |
static boolean |
isReorderingEnabled()
Returns whether or not state-changing operations and grouping operations automatically change the hierarchic order of nodes. |
boolean |
isRootGraph(Graph graph)
Returns whether or not the given graph is the root graph of this hierarchy. |
void |
moveToFirst(Node childNode)
Makes the given node the first child of its parent. |
void |
moveToLast(Node childNode)
Makes the given node the last child of its parent. |
void |
openFolder(Node folderNode)
Convenience method that performs all necessary steps to convert a folder node to a group node. |
java.util.Iterator |
postTraversal()
Post-traverse all nodes within the hierarchy. |
java.util.Iterator |
postTraversal(Node rootNode)
Post-traverse all nodes within the hierarchy that are descendants of the given group or folder node. |
void |
postTraverse(HierarchyManager.NodeVisitor visitor)
Post-traverse all nodes within the hierarchy. |
void |
postTraverse(Node rootNode,
HierarchyManager.NodeVisitor visitor)
Post-traverse all nodes within the hierarchy, that are descendants of the given group or folder node. |
java.util.Iterator |
preTraversal()
Pre-traverse all nodes within the hierarchy. |
java.util.Iterator |
preTraversal(Node rootNode)
Pre-traverse all nodes within the hierarchy that are descendants of the given group or folder node. |
void |
preTraverse(HierarchyManager.NodeVisitor visitor)
Pre-traverse all nodes within the hierarchy. |
void |
preTraverse(Node rootNode,
HierarchyManager.NodeVisitor visitor)
Pre-traverse all nodes within the hierarchy, that are descendants of the given group or folder node. |
void |
reInsertEdge(Edge e,
Node src,
Node tgt)
Reinserts the formerly removed specified edge into this HierarchyManager's graph hierarchy. |
void |
removeFolderNode(Node folderNode)
Removes the given node from the graph if it is a folder node. |
void |
removeGroupNode(Node groupNode)
Removes the given group node and all of its descendants within the group node's graph. |
void |
removeHierarchyListener(HierarchyListener listener)
Removes the given HierarchyListener from the list of registered listeners of this HierarchyManager. |
void |
setGraphFactory(GraphFactory factory)
Sets the graph factory used by this manager to create new nodes and graphs. |
void |
setInterEdgeConfigurator(InterEdgeConfigurator interEdgeConfigurator)
Sets the InterEdgeConfigurator for this class. |
void |
setParentNode(NodeList nodeList,
Node parentNode)
Assigns the nodes contained in nodeList to a group or folder that is
represented by the given parentNode. |
void |
setParentNode(Node v,
Node parentNode)
Assigns v to a group or folder that is represented by the given parent node. |
static void |
setReorderingEnabled(boolean enabled)
Specifies whether or not state-changing operations and grouping operations should automatically change the hierarchic order of nodes. |
void |
unfoldSubgraph(Graph innerGraph,
NodeList subNodes)
Moves part of a nested graph up the hierarchy to the parent graph. |
void |
ungroupSubgraph(NodeList subNodes)
Convenience method that moves all given nodes a hierarchy level up, if possible. |
| Methods inherited from class java.lang.Object |
|---|
clone, equals, finalize, getClass, hashCode, notify, notifyAll, toString, wait, wait, wait |
| Constructor Detail |
|---|
public HierarchyManager(Graph rootGraph)
DefaultHierarchyGraphFactory is used by default.
Note that there must not be more than one HierarchyManager instance associated with a given root graph.
rootGraph - The root graph for the hierarchy manager to manage.HierarchyManager(Graph, GraphFactory),
getInstance(Graph)
public HierarchyManager(Graph root,
GraphFactory factory)
The given graph factory is used by this manager to create new nodes and graphs. The graph factory is responsible for creating the right kind of node and graph elements within this hierarchy. The factory is also responsible for propagating registered listeners from the parent graph to the newly generated graphs.
The hierarchy manager passes certain hints to
the registered graph factory. If the hint for node creation is
of type Graph, then the created node will be a folder node whose
inner graph is represented by the hint.
The hint for graph creation is always the parent graph of the newly
created graph.
By default a factory of type DefaultHierarchyGraphFactory is set.
Note that there must not be more than one HierarchyManager instance associated with a given root graph.
getInstance(Graph)| Method Detail |
|---|
public static HierarchyManager getInstance(Graph graph)
graph - a graph whose associated hierarchy manager is being sought.
null in case the given graph is not part of a hierarchy.public void dispose()
Note: Calling this method will deregister this manager from an
associated Graph2D instance, i.e.
Graph2D.getHierarchyManager() will return null
after calling dispose if the graph's hierarchy manager has not
already been replaced.
public Node createFolderNode(Node parent)
GraphFactory is responsible for both
the creation of the new inner graph accessible by the folder node and
the folder node itself.
Emits a HierarchyEvents of type HierarchyEvent.PRE_NODE_STATE_CHANGE,
and HierarchyEvent.NODE_STATE_CHANGED.
parent - the node that represents the graph in which to create the folder node.
public Node createFolderNode(Graph parentGraph)
createFolderNode(Node). The newly created folder node will
be created as a child node of getAnchorNode(parentGraph)).
public void removeFolderNode(Node folderNode)
Graph.removeNode(y.base.Node) on the
given folder node.
folderNode - the folder node that shall be removed.public Node createGroupNode(Node parent)
GraphFactory is responsible for the creation
and configuration of the group node.
Emits a HierarchyEvent of type HierarchyEvent.PRE_NODE_STATE_CHANGE and
HierarchyEvent.NODE_STATE_CHANGED.
parent - the group or folder node that will be the parent of
the newly created node.
public void removeGroupNode(Node groupNode)
groupNode - the group node that shall be removed.public Node createGroupNode(Graph graph)
createGroupNode(Node). The newly created group node will
be created as a child node of getAnchorNode(parentGraph)).
public void convertToGroupNode(Node v)
Note that this method only changes the hierarchy state of the converted node. In particular, it does
not change the realizer of a node which belongs to a Graph2D.
Emits HierarchyEvents of type HierarchyEvent.PRE_NODE_STATE_CHANGE
and HierarchyEvent.NODE_STATE_CHANGED.
v - a folder node or a normal node that should be converted to a group node
public Edge createEdge(Node v,
Node w)
common ancestor only.
In the case where they don't lie in the same graph an inter-edge is automatically
created.
v - the first or source nodew - the second or target node
representative nodes in the common ancestor graph
public void changeEdge(Edge e,
Node src,
Node tgt)
HierarchyManager's graph hierarchy. If necessary, the edge is
removed from its original graph and reinserted in the
nearest
common ancestor graph of the specified nodes.
If the specified edge is a normal edge (i.e. it is not an inter-edge), but the specified nodes belong to different graphs, this method automatically converts the edge to an inter-edge. If the specified edge is an inter-edge and the specified nodes belong to different graphs, this method ensures that all inter-edge data associated to the edge is retained when changing the edge's (real) end points. If the specified edge is an inter-edge and the specified nodes belong to one graph, the edge is converted to a normal edge and all inter-edge data previously associated to the edge is lost.
e - the edge to be changed.src - the new (real) source node of the edge.tgt - the new (real) target node of the edge.
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException - if the specified edge, source, or target
node belong to a graph that is not part of this graph hierarchy or if one
or both of the given nodes belong to no graph at all.getRealSource(y.base.Edge),
getRealTarget(y.base.Edge),
getInterEdgeData(y.base.Edge),
Graph.changeEdge(y.base.Edge, y.base.Node, y.base.Node)
public void reInsertEdge(Edge e,
Node src,
Node tgt)
HierarchyManager's graph hierarchy.
The specified nodes may belong to any graph in this
HierarchyManager's graph hierarchy.
If the specified edge was an inter-edge before removing it from its graph and the specified nodes belong to different graphs, this method ensures that all inter-edge data associated to the edge is retained when re-inserting the edge. If the specified edge was an inter-edge before removing it from its graph and the specified nodes belong to one graph, all inter-edge data previously associated to the edge is lost when re-inserting the edge.
e - the edge to be inserted.src - the (new real) source node of the edge.tgt - the (new real) target node of the edge.
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException - if the specified edge already belongs to
a graph or if source or target node belong to a graph that is not part of
this graph hierarchy or if one or both of the given nodes belong to no
graph at all.getRealSource(y.base.Edge),
getRealTarget(y.base.Edge),
getInterEdgeData(y.base.Edge),
Graph.reInsertEdge(y.base.Edge)
public Node getRepresentative(Node v,
Graph inGraph)
Node representing a Node
in another Graph if the node lies in that graph is an ancestor of the node.
v - the node whose representative will be returnedinGraph - the graph for which an representative is sought
inGraph and is either v
itself or an ancestor folder node of vpublic void convertToFolderNode(Node v)
Note that this method only changes the hierarchy state of the converted node. In particular, it does
not change the realizer of a node which belongs to a Graph2D.
Emits HierarchyEvents of type HierarchyEvent.PRE_NODE_STATE_CHANGE
and HierarchyEvent.NODE_STATE_CHANGED.
v - a group node or a normal node that should be converted to a folder nodeconvertToFolderNode(y.base.Node, y.base.Graph)
public void convertToFolderNode(Node v,
Graph innerGraph)
convertToFolderNode(y.base.Node) with the additional option to
specify the inner graph to be used by the folder node.
convertToFolderNode(y.base.Node)public void closeGroup(Node groupNode)
groupNode - the group node to be closedpublic void openFolder(Node folderNode)
folderNode - the folder node to be openedpublic void convertToNormalNode(Node v)
Emits HierarchyEvents of type HierarchyEvent.PRE_NODE_STATE_CHANGE
and HierarchyEvent.NODE_STATE_CHANGED.
public void convertToInterEdge(Edge e,
Node realSource,
Node realTarget)
The specified real source node must be either identical with the source node of the given edge or the real source node must be contained within the graph hierarchy subtree reachable from the source node of the given edge. The same applies to the given real target node.
The given edge must be a normal edge.
e - the edge to be converted to an inter-edgerealSource - the real source node associated with the
inter-edgerealTarget - the real target node associated with the
inter-edgepublic void convertToNormalEdge(Edge e)
e - the edge to be converted to a normal edgepublic void setGraphFactory(GraphFactory factory)
A hierarchy manager passes certain hints to the registered graph factory. If the hint for node creation is of type Graph then the created node will be a folder node whose inner graph is represented by the hint. The hint for graph creation is always the parent graph of the newly created graph.
By default a factory of type DefaultHierarchyGraphFactory is set.
public GraphFactory getGraphFactory()
setGraphFactory(GraphFactory)public InterEdgeConfigurator getInterEdgeConfigurator()
public void setInterEdgeConfigurator(InterEdgeConfigurator interEdgeConfigurator)
DefaultInterEdgeConfigurator is set.
public void preTraverse(HierarchyManager.NodeVisitor visitor)
public void preTraverse(Node rootNode,
HierarchyManager.NodeVisitor visitor)
public void postTraverse(HierarchyManager.NodeVisitor visitor)
public void postTraverse(Node rootNode,
HierarchyManager.NodeVisitor visitor)
public java.util.Iterator preTraversal()
Iterator
created by this method visits the descendants of a node only after the node
has been visited. Also, the children of a node will be visited from first
to last child.
public java.util.Iterator preTraversal(Node rootNode)
Iterator created by this method visits the descendants of
a node only after the node has been visited. Also, the children of a node
will be visited from first to last child.
public java.util.Iterator postTraversal()
Iterator
created by this method visits a node only after all of its descendant nodes
have been visited. Also, the children of a node will be visited from last
to first child.
public java.util.Iterator postTraversal(Node rootNode)
Iterator created by this method visits a node only after
all of its descendant nodes have been visited. Also, the children of a
node will be visited from last to first child.
public DataProvider getNodeIdDataProvider()
public DataProvider getParentNodeIdDataProvider()
getNodeIdDataProvider().get(getParentNode(v)) == getParentNodeDataProvider().get(v)
getNodeIdDataProvider()public DataProvider getGroupNodeDataProvider()
isGroupNode(v) == getGroupNodeDataProvider().getBool(v)
public static boolean containsGroupNodes(Graph graph)
public Node getRealSource(Edge e)
e - the inter-edge for which to return the real source nodepublic Node getRealTarget(Edge e)
e - the inter-edge for which to return the real target nodepublic boolean contains(Graph graph)
public HierarchyManager.InterEdgeData getInterEdgeData(Edge e)
Note: Client code should not hold onto data objects returned by this method as subsequent calls are neither guaranteed to return (referentially) different objects for different edges nor guaranteed to return (referentially) equal objects for one and the same edge.
e - the inter-edge for which to return a data object.
null if the specified edge is
no inter-edge.isInterEdge(y.base.Edge)public boolean isInterEdge(Edge e)
public boolean isFolderNode(Node v)
public boolean isGroupNode(Node v)
public boolean isNormalNode(Node v)
public boolean containsGroups()
public Graph getInnerGraph(Node folderNode)
folderNode - the anchor node.
public Node getAnchorNode(Graph graph)
null gets returned.
Otherwise a folder node whose inner graph is the given graph
will be returned.
public Node getParentNode(Node node)
null if the given node has no parent node. In such a case
the node belongs to the root graph.
public boolean isAncestor(Node presumedAncestor,
Node node)
presumedAncestor - the presumed ancestor of nodenode - the presumed descendant of presumedAncestorpublic Graph getParentGraph(Graph graph)
public Graph getRootGraph()
public boolean isRootGraph(Graph graph)
public java.lang.Object[] getFolderPath(java.lang.Object item)
item - either a graph within this hierarchy or a node contained in such a graph.
public java.lang.Object[] getTreePath(java.lang.Object item)
item - either a graph within this hierarchy or a node contained in such a graph.
public java.lang.Object[] getTreePath(java.lang.Object item,
boolean includeItem)
getTreePath(Object) with the additional option to
include the given item as the last element of the path.
includeItem - whether or not to include the given item as the last
element of the path.public Node getNearestCommonAncestor(NodeList subNodes)
subNodes - arbitrary nodes being part of this hierarchy.
nullwill
be returned.
public Graph getNearestCommonAncestor(Graph g1,
Graph g2)
g1 - the first graphg2 - the second graph
public NodeList getFolderNodes(Graph rootGraph,
boolean recursive)
The result will be returned as an ordered list of nodes. The order of nodes is such that a hierarchically higher folder node will always occur before a hierarchically lower node in the list.
public int getLocalGroupDepth(Node node)
0. If it parent node
of the given node is a group node p then the result will be
the same as the one for p plus 1.
public NodeCursor getChildren(Node node)
public void addHierarchyListener(HierarchyListener listener)
public void removeHierarchyListener(HierarchyListener listener)
public java.util.Iterator getHierarchyListeners()
protected void fireHierarchyEvent(HierarchyEvent e)
public void moveToFirst(Node childNode)
postTraverse(y.view.hierarchy.HierarchyManager.NodeVisitor),
preTraverse(y.view.hierarchy.HierarchyManager.NodeVisitor)public void moveToLast(Node childNode)
postTraverse(y.view.hierarchy.HierarchyManager.NodeVisitor),
preTraverse(y.view.hierarchy.HierarchyManager.NodeVisitor)
public void foldSubgraph(NodeList subNodes,
Node folderNode)
Edges that have exactly one end point within the moved subgraph will be redefined, in such a way that the edge will have both of it's end points within the same graph. Edges that stay within the parent graph will be redefined to have one end point to be the given folder node. If both end points of the edge lie somewhere within the given folder node after the operation, then the edge will be redefined as well.
public void unfoldSubgraph(Graph innerGraph,
NodeList subNodes)
foldSubgraph(NodeList, Node).
The given graph must have a parent graph.
The effect of the method calls
foldSubGraph(subNodes, folderNode) unfoldSubGraph(getInnerGraph(folderNode), subNodes)first folds and then unfolds a subgraph again. The graphs and graph hierarchy will appear unchanged after this call sequence.
The given graph must have a parent graph
innerGraph - the nested graph that is the source of the subgraph movementsubNodes - nodes within graph that will be moved to the parent graph
public void setParentNode(NodeList nodeList,
Node parentNode)
nodeList to a group or folder that is
represented by the given parentNode. The parentNode may either be a group node,
a folder node or null, where null denotes the root graph.
nodeList - a list of nodes that is assigned to a new group or folderparentNode - the node that represents a group or folder.
public void setParentNode(Node v,
Node parentNode)
v to a group or folder that is represented by the given parent node.
The parent node may either be a group node, a folder node or null, where
null denotes the root graph.
v - the node that is assigned to a new group or folderparentNode - new parent node that represents a group or folder.
public void groupSubgraph(NodeList subNodes,
Node groupNode)
public void ungroupSubgraph(NodeList subNodes)
1, if it is not already 0.
getLocalGroupDepth(Node).public static boolean isReorderingEnabled()
createFolderNode,createGroupNode,convertToFolderNode,convertToGroupNode,convertToNormalNode,closeGroup, andopenFoldergroupSubgraph andungroupSubgraphAs of yFiles for Java 2.11, reordering is disabled by default.
Client code should only enable reordering in legacy applications that
require the traversal methods
preTraversal, postTraversal,
preTraverse, and postTraverse
to report folder and group child nodes before normal child nodes for any
given hierarchy level.
true if state-changing operations and
grouping operations automatically change the hierarchic order of nodes;
false otherwise.setReorderingEnabled(boolean)public static void setReorderingEnabled(boolean enabled)
createFolderNode,createGroupNode,convertToFolderNode,convertToGroupNode,convertToNormalNode,closeGroup, andopenFoldergroupSubgraph andungroupSubgraphAs of yFiles for Java 2.11, reordering is disabled by default.
Client code should only enable reordering in legacy applications that
require the traversal methods
preTraversal, postTraversal,
preTraverse, and postTraverse
to report folder and group child nodes before normal child nodes for any
given hierarchy level.
enabled - if true, state-changing operations and
grouping operations will automatically change the hierarchic order of nodes.isReorderingEnabled()
|
© Copyright 2000-2025, yWorks GmbH. All rights reserved. |
||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | ||||||||
| SUMMARY: NESTED | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | ||||||||