 y.layout.router.polyline.PathSearch
y.layout.router.polyline.PathSearch
|
Search this API | ||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | ||||||||
| SUMMARY: NESTED | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | ||||||||
java.lang.Objecty.layout.router.polyline.PathSearch
public class PathSearch
This is a pathfinding algorithm that calculates the shortest (i.e., the cheapest) paths for a set of edges through a
GraphPartition.
It is based on an A*-algorithm and uses
PartitionCells as steps between source node and target node.
In each step, the algorithm takes a CellEntrance, that consists mainly of a PartitionCell and
from where it was entered, from a queue with all seen CellEntrances, determines all possible neighbor
cells and their enter intervals and enqueues the resulting CellEntrance.
To influence the order in which the CellEntrances will be processed, the path search assigns real
costs (like Dijkstra) as well as heuristic costs (A*-algorithm's heuristic) to the enqueued
CellEntrances. The real costs arise from entering a neighbor cell, e.g., a bend has to be created,
while the heuristic costs are an estimation of how expensive it will be to reach the target node continuing the
path with this neighboring cell. Therefore, the path search prefers searching in the direction in which the target node
lies. The CellEntrance with the lowest combined costs is processed next until the target cell is reached.
PathSearchExtensions modify the path search as they are able to add start
entrances and weight them with costs. They also add real and heuristic costs to CellEntrances that are
created for the currently entered PartitionCell and calculate shorter enter intervals that are less
expensive to pass.
The algorithm gets a PathSearchContext which provides information about the graph and the currently routed
edge. It stores the results of the path search that can then be retrieved calling
PathSearchContext.getPathSearchResult().
addPathSearchExtension(PathSearchExtension),
addAdditionalEnterIntervalCalculator(EnterIntervalCalculator)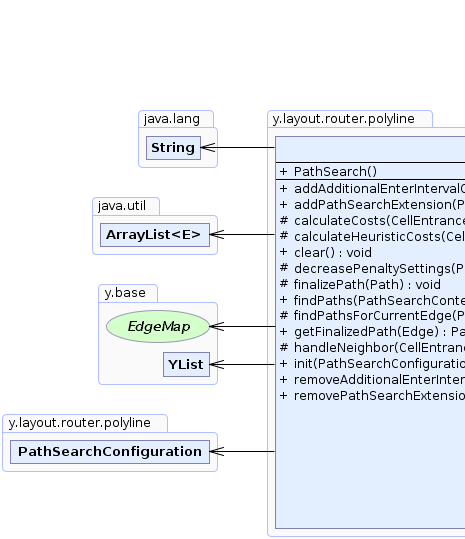 |
 |
 |
| Constructor Summary | |
|---|---|
PathSearch()
Creates a new instance of PathSearch. |
|
| Method Summary | |
|---|---|
boolean |
addAdditionalEnterIntervalCalculator(EnterIntervalCalculator enterIntervalCalculator)
Adds a new interval calculator to the list of registered EnterIntervalCalculators. |
boolean |
addPathSearchExtension(PathSearchExtension extension)
Adds the given extension to the list of PathSearchExtensions. |
protected void |
calculateCosts(CellEntrance currentEntrance,
PartitionCell enteredCell,
OrthogonalInterval[] enterIntervals,
EdgeCellInfo[] lastEdgeCellInfos,
PathSearchContext context,
double[] costs,
double[] maxAllowedCosts)
Calculates the costs for moving from the current CellEntrance to the neighboring PartitionCell using
different enter intervals. |
protected double |
calculateHeuristicCosts(CellEntrance entrance,
PathSearchContext context)
Returns the estimated costs for the rest of the path when using the given CellEntrance for the next step in
the path search. |
void |
clear()
Resets all registered PathSearchExtensions and DataProviders added to this PathSearch. |
protected void |
decreasePenaltySettings(PenaltySettings penaltySettings,
double decreaseFactor,
PathSearchContext context)
Decreases the given penalty settings for the current edge. |
protected void |
finalizePath(Path path)
Informs all registered path search extensions about completing a path by calling their finalizePath(Path) method. |
void |
findPaths(PathSearchContext context)
Finds paths for the edges in the given context and stores them in its PathSearchResult. |
protected void |
findPathsForCurrentEdge(PathSearchContext context)
Finds the path for the current edge in the given context. |
Path |
getFinalizedPath(Edge edge)
Returns the path for the given edge if it has already been finalized. |
protected void |
handleNeighbor(CellEntrance currentEntrance,
PartitionCell neighborCell,
PathSearchContext context)
Adds CellEntrances for every interval through which the neighboring cell can be entered from the current
entrance to the queue. |
void |
init(PathSearchConfiguration configuration)
Initializes the fields of this PathSearch. |
boolean |
removeAdditionalEnterIntervalCalculator(EnterIntervalCalculator enterIntervalCalculator)
Removes the given interval calculator from the list of registered EnterIntervalCalculators. |
boolean |
removePathSearchExtension(PathSearchExtension extension)
Removes the given extension from the list of PathSearchExtensions. |
| Methods inherited from class java.lang.Object |
|---|
clone, equals, finalize, getClass, hashCode, notify, notifyAll, toString, wait, wait, wait |
| Constructor Detail |
|---|
public PathSearch()
PathSearch.
| Method Detail |
|---|
public boolean addPathSearchExtension(PathSearchExtension extension)
PathSearchExtensions.
An extension can influence the pathfinding process by adding costs for entering certain CellEntrances.
extension - the extension to add to this path search
true if the extension has been added, false otherwisepublic boolean removePathSearchExtension(PathSearchExtension extension)
PathSearchExtensions.
extension - the extension to remove from the path search
true if an extension was removed as a result of this call, false if the given
extension was not contained in the listpublic boolean addAdditionalEnterIntervalCalculator(EnterIntervalCalculator enterIntervalCalculator)
EnterIntervalCalculators.
EnterIntervalCalculators may add CellEntrances with narrowed intervals to the queue. The interval
is more specific and will be judged with lower costs.
enterIntervalCalculator - the calculator to add
true if the calculator was successfully added, false otherwisepublic boolean removeAdditionalEnterIntervalCalculator(EnterIntervalCalculator enterIntervalCalculator)
EnterIntervalCalculators.
enterIntervalCalculator - the calculator to remove
true if an interval calculator was removed as a result of this call, false if the
given calculator was not part of the listpublic void init(PathSearchConfiguration configuration)
PathSearch.
This method also calls PathSearchExtension.initialize(PathSearchConfiguration) for all registered
path search extensions.
configuration - the configuration that the path search shall usepublic void clear()
PathSearchExtensions and DataProviders added to this PathSearch. So,
PathSearch is ready to calculate paths for a new layout.
PathSearchExtension.cleanup()public Path getFinalizedPath(Edge edge)
The path is finalized if the PathSearch chose it as the best result for the edge.
edge - the edge for which the path is returned
null if no path has been found and finalizedprotected void findPathsForCurrentEdge(PathSearchContext context)
PathSearchExtension.initializeCurrentEdge(PathSearchContext) for all extensions.finalizePath(Path) call if it is a valid target entrance and/orhandleNeighbor(CellEntrance, PartitionCell, PathSearchContext) for all neighbor cells of the entered cell.PathSearchExtension.finalizeCurrentEdge(PathSearchContext) for all extensions.
It is called by findPaths(PathSearchContext) and may be overridden to skip certain edges or implement a
custom path search.
context - the context information needed for finding a path
protected void decreasePenaltySettings(PenaltySettings penaltySettings,
double decreaseFactor,
PathSearchContext context)
If finding a path for the current edge takes too long according to the
maximum duration of the edge routing algorithm,
the path search for the current edge is canceled and restarted using decreased penalties. The
decreaseFactor indicates, how much the penalties shall be reduced.
This method is called by findPathsForCurrentEdge(PathSearchContext).
If overriding this method, note that the penalty for creating bends should not be reduced as this results
in more possible turns of the edge path and, therefore, a longer runtime of the path search. Furthermore, not all
penalties should be decreased equally as these decreases would neutralize each other.
The decreaseFactor takes values from [0,1], where 0 means no reduction
while 1 means the strongest reduction.
penaltySettings - the penalty settings whose penalties shall be reduceddecreaseFactor - the factor with values between 0 and 1 that indicates how strong
to reduce the penaltiescontext - the context information of the current path searchpublic void findPaths(PathSearchContext context)
PathSearchResult.
This is the main method of PathSearch.
It initializes its extensions using PathSearchExtension.initializeEdges(PathSearchContext) and
delegates the path search for each edge to findPathsForCurrentEdge(PathSearchContext).
The path calculations for all edges are finalized by calling the extensions'
PathSearchExtension.finalizeEdges(PathSearchContext) method and, after that, the path search result
is filled with the path for each edge.
At last, the extensions are asked to finalize the path search result using their
PathSearchExtension.finalizePathSearchResult(PathSearchResult) callback.
context - the context to use during the path searchPathSearchContext.getEdges(),
PathSearchContext.getPathSearchResult()protected void finalizePath(Path path)
finalizePath(Path) method. That way, extensions can collect data
about this path to use it later during path search.
This method is called by findPathsForCurrentEdge(PathSearchContext) and may be overridden to use a
custom finalization step.
path - the path to finalize
protected void handleNeighbor(CellEntrance currentEntrance,
PartitionCell neighborCell,
PathSearchContext context)
CellEntrances for every interval through which the neighboring cell can be entered from the current
entrance to the queue. The algorithm calls this method in every step for each neighbor of the current cell to
collect all next possible entrances for the current path. This path consists of several entrances where each knows
the entrance through which it has been entered.
After calculating all possible enter intervals to the given neighboring cell, each interval gets rated with costs. If there is already an entrance for the neighboring cell whose interval is the same with one of these intervals, this entrance will be used and re-enqueued, so that the path search can still reach it. The current entrance is set as its predecessor within the current path and its enter interval and costs will be updated.
If there is an entrance for the neighboring cell whose interval is intersected by a current interval, new entrances will be created with the new enter intervals and enqueued. The same happens if there is no entrance that has been matched with one of the current intervals, yet. Costs will be added. If there are some entries afterwards that are intersected by the current interval and have higher costs, they will be removed from the queue.
This method is called during cost calculation. It may be overridden to change the interval handling for the
CellEntrances.
currentEntrance - the current cell entranceneighborCell - the neighboring cell that is handled.context - the context informationcalculateCosts(CellEntrance, PartitionCell, OrthogonalInterval[], EdgeCellInfo[], PathSearchContext, double[], double[]),
calculateHeuristicCosts(CellEntrance, PathSearchContext)
protected void calculateCosts(CellEntrance currentEntrance,
PartitionCell enteredCell,
OrthogonalInterval[] enterIntervals,
EdgeCellInfo[] lastEdgeCellInfos,
PathSearchContext context,
double[] costs,
double[] maxAllowedCosts)
CellEntrance to the neighboring PartitionCell using
different enter intervals. It is called by handleNeighbor(CellEntrance, PartitionCell, PathSearchContext)
to determine the costs for all CellEntrances that it will create and enqueue afterwards.
The costs for the given enter intervals are retrieved from all registered PathSearchExtensions. The
calculation stops when it reaches the given maximum cost value.
currentEntrance - the current cell entranceenteredCell - the partition cell to enterenterIntervals - the different entering intervals of the entered celllastEdgeCellInfos - the information about how the last cell was crossedcontext - the context informationcosts - the array in which the calculated costs for entering the neighbor cell via the according enter
intervals shall be writtenmaxAllowedCosts - the maximum costs an enter interval may induce. If this cost is exceeded, no further
additional costs for this interval are calculated. Note that the entries in this
array get modified during cost calculationPathSearchExtension.calculateCosts(CellEntrance, PartitionCell, OrthogonalInterval, EdgeCellInfo, double)
protected double calculateHeuristicCosts(CellEntrance entrance,
PathSearchContext context)
CellEntrance for the next step in
the path search. It is called by handleNeighbor(CellEntrance, PartitionCell, PathSearchContext)
to determine the heuristic part of the costs with which the entrance will be enqueued.
The heuristic costs for the given entrance are retrieved from all registered PathSearchExtensions.
entrance - the current entrancecontext - the context information
PathSearchExtension.calculateHeuristicCosts(CellEntrance)
|
© Copyright 2000-2025, yWorks GmbH. All rights reserved. |
||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | ||||||||
| SUMMARY: NESTED | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | ||||||||