 y.layout.AbstractLayoutStage
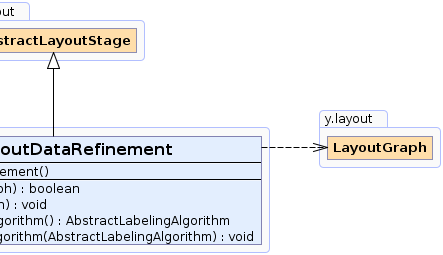
y.layout.AbstractLayoutStage
 y.layout.LabelLayoutDataRefinement
y.layout.LabelLayoutDataRefinement
|
Search this API | ||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | ||||||||
| SUMMARY: NESTED | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | ||||||||
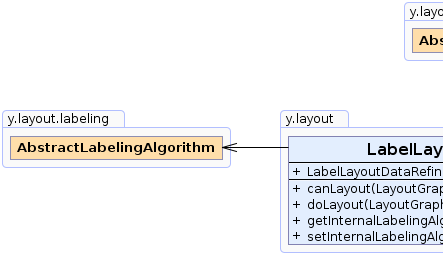
java.lang.Objecty.layout.AbstractLayoutStage
y.layout.LabelLayoutDataRefinement
public class LabelLayoutDataRefinement
LabelLayoutDataRefinement improves the placement of edge labels.
This LayoutStage requires that its core layout algorithm calculates initial edge
LabelLayoutData instances bound to a DataProvider registered with key
LabelLayoutKeys.EDGE_LABEL_LAYOUT_KEY. Then, it tries to improve the position of the labels with respect to
their preferred placement.
HierarchicLayouter.
The following code snippet shows how this layout stage can be set up:
// 'hierarchic' is of type y.layout.hierarchic.HierarchicLayouter. // String together a label layout process. CompositeLayoutStage ll = new CompositeLayoutStage(); ll.appendStage(new LabelLayoutTranslator()); ll.appendStage(new LabelLayoutDataRefinement()); // Set the compound label layout process as the label layouter for // HierarchicLayouter. hierarchic.setLabelLayouter(ll); hierarchic.setLabelLayouterEnabled(true);
 |
 |
| Field Summary |
|---|
| Fields inherited from interface y.layout.Layouter |
|---|
EDGE_ID_DPKEY, NODE_ID_DPKEY, NODE_TYPE_DPKEY, SELECTED_EDGES, SELECTED_NODES |
| Constructor Summary | |
|---|---|
LabelLayoutDataRefinement()
Creates a new LabelLayoutDataRefinement instance with default settings. |
|
| Method Summary | |
|---|---|
boolean |
canLayout(LayoutGraph graph)
Accepts all general graphs. |
void |
doLayout(LayoutGraph graph)
Improves the labeling after invoking the core layout algorithm. |
AbstractLabelingAlgorithm |
getInternalLabelingAlgorithm()
Returns the internal labeling algorithm that will improve the label positions. |
void |
setInternalLabelingAlgorithm(AbstractLabelingAlgorithm labeler)
Specifies the internal labeling algorithm that will improve the label positions. |
| Methods inherited from class y.layout.AbstractLayoutStage |
|---|
canLayoutCore, doLayoutCore, getCoreLayouter, setCoreLayouter |
| Methods inherited from class java.lang.Object |
|---|
clone, equals, finalize, getClass, hashCode, notify, notifyAll, toString, wait, wait, wait |
| Constructor Detail |
|---|
public LabelLayoutDataRefinement()
LabelLayoutDataRefinement instance with default settings.
| Method Detail |
|---|
public void setInternalLabelingAlgorithm(AbstractLabelingAlgorithm labeler)
GreedyMISLabelinglabeler - the labeling algorithmpublic AbstractLabelingAlgorithm getInternalLabelingAlgorithm()
setInternalLabelingAlgorithm(AbstractLabelingAlgorithm)public boolean canLayout(LayoutGraph graph)
graph - the input graph
true for all graphsLayouter.doLayout(LayoutGraph)public void doLayout(LayoutGraph graph)
core layout algorithm.
core layout algorithm must provide a DataProvider
registered with the input graph with LabelLayoutKeys.EDGE_LABEL_LAYOUT_KEY. This
DataProvider must hold arrays of LabelLayoutData instances. Otherwise, the call to this
method will not succeed.graph - the input graphLayouter.canLayout(LayoutGraph)
|
© Copyright 2000-2025, yWorks GmbH. All rights reserved. |
||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | ||||||||
| SUMMARY: NESTED | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | ||||||||