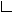 y.layout.EdgeBundling
y.layout.EdgeBundling
|
Search this API | ||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | ||||||||
| SUMMARY: NESTED | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | ||||||||
java.lang.Objecty.layout.EdgeBundling
public class EdgeBundling
An EdgeBundling instance defines if and how the edges of a graph should be bundled by a
layout algorithm, given that the algorithm supports edge bundling.
Bundling together multiple edges means that their common parts are to some degree merged into a bundled part. At the source and target point, the edges are again clearly split. Edge bundling is useful to increase the readability of graph drawings with a high number of edges that connect a comparably small number of nodes. Without bundling, such drawings can often contain visual clutter and feature bad readability.
The bundling strength and quality are
global settings for the bundling process. On the other hand, each edge can get specific settings by
assigning a EdgeBundleDescriptor to it. A DataProvider can be registered with
the input graph with key EDGE_BUNDLE_DESCRIPTOR_DPKEY to assign descriptors to edges.
This allows, for example, to define which edges should actually be bundled.
The following layout algorithms/stages currently support bundling.
CircularLayouter
RadialLayouter
TreeReductionStage: only for graphs that do not contain multi-parent structures
EdgeBundlingStage: a generic bundling stage, any core layout algorithm may be used

CircularLayouter
TreeReductionStage and BalloonLayouter on a general graph
EdgeBundleDescriptor,
CircularLayouter.getEdgeBundling(),
RadialLayouter.getEdgeBundling(),
TreeReductionStage.getEdgeBundling(),
EdgeBundlingStage.getEdgeBundling() |
 |
| Field Summary | |
|---|---|
static java.lang.Object |
EDGE_BUNDLE_DESCRIPTOR_DPKEY
A DataProvider key for specifying individual bundling settings for edges
If no EdgeBundleDescriptor is mapped to an edge, the default
descriptor is used by the layout algorithm to obtain the bundling setup of that edge. |
| Constructor Summary | |
|---|---|
EdgeBundling()
Creates a new EdgeBundling instance with default settings. |
|
EdgeBundling(double bundlingStrength,
double bundlingQuality)
Creates a new EdgeBundling instance with the given bundling strength
and bundling quality. |
|
| Method Summary | |
|---|---|
double |
getBundlingQuality()
Returns the desired quality of the calculated edge bundling. |
double |
getBundlingStrength()
Returns the strength of the edge bundling. |
EdgeBundleDescriptor |
getDefaultBundleDescriptor()
Returns the default EdgeBundleDescriptor used for all edges which do not have a specific
descriptor assigned via a DataProvider registered with key EDGE_BUNDLE_DESCRIPTOR_DPKEY. |
void |
setBundlingQuality(double bundlingQuality)
Specifies the desired quality of the calculated edge bundling. |
void |
setBundlingStrength(double bundlingStrength)
Specifies the strength of the edge bundling. |
void |
setDefaultBundleDescriptor(EdgeBundleDescriptor defaultBundleDescriptor)
Specifies the default EdgeBundleDescriptor used for all edges which do not have a specific
descriptor assigned via a DataProvider registered with key EDGE_BUNDLE_DESCRIPTOR_DPKEY. |
| Methods inherited from class java.lang.Object |
|---|
clone, equals, finalize, getClass, hashCode, notify, notifyAll, toString, wait, wait, wait |
| Field Detail |
|---|
public static final java.lang.Object EDGE_BUNDLE_DESCRIPTOR_DPKEY
DataProvider key for specifying individual bundling settings for edges
If no EdgeBundleDescriptor is mapped to an edge, the default
descriptor is used by the layout algorithm to obtain the bundling setup of that edge.
getDefaultBundleDescriptor()| Constructor Detail |
|---|
public EdgeBundling()
EdgeBundling instance with default settings.
public EdgeBundling(double bundlingStrength,
double bundlingQuality)
EdgeBundling instance with the given bundling strength
and bundling quality.
bundlingStrength - the bundling strength from the interval [0,1]bundlingQuality - the bundling quality from the interval [0,1]
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException - if the given bundling strength or quality is not within [0,1]| Method Detail |
|---|
public double getBundlingQuality()
Higher quality indicates that the bundling procedure uses more sophisticated methods to compute the
actual bundles and the routing of the edges. If the applied layout algorithm is the
CircularLayouter, this may lead to a significantly higher running time, especially
for large graphs. On the other hand, a low quality indicates that run-time is more important than
highly optimized bundling results, leading to, for example, more crossings between different bundles
(for CircularLayouter) or completely straight-line un-bundled edges for
the EdgeBundlingStage.
The quality is defined to lie within [0,1], where higher values stand for higher quality.
CircularLayouter or the EdgeBundlingStage.0 (low quality, fast) and 1 (high quality, slow)setBundlingQuality(double)public void setBundlingQuality(double bundlingQuality)
Higher quality indicates that the bundling procedure uses more sophisticated methods to compute the
actual bundles and the routing of the edges. If the applied layout algorithm is the
CircularLayouter, this may lead to a significantly higher running time, especially
for large graphs. On the other hand, a low quality indicates that run-time is more important than
highly optimized bundling results, leading to, for example, more crossings between different bundles
(for CircularLayouter) or completely straight-line un-bundled edges for
the EdgeBundlingStage.
The quality is defined to lie within [0,1], where higher values stand for higher quality.
CircularLayouter or the EdgeBundlingStage.bundlingQuality - a value between 0 (low quality, fast) and 1 (high quality, slow)
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException - if the given quality value is not within [0,1]public double getBundlingStrength()
The strength controls how tightly the edges are bundled and influences the shape of the curves of bundled edges. Low values lead to only slightly bundled edges; results will mostly show individual node-to-node connectivity information. High values show the connectivity on a higher level, strongly bundling edges together and generating highly curved edge paths.
The bundling strength is defined as a value from the interval [0,1].
EdgeBundlingStage, to obtain results
with clearly observable larger bundles, it is recommended to use a strength value of 0.8 or higher.
For the EdgeBundlingStage, it is recommended to use a value, close to 0.4.0 leads to straight-line edges where edges are basically not bundled.EdgeBundlingStage, high values can significantly affect the
performance of the algorithm, especially for large graphs.0 (no bundling) and 1 (strongly bundled edges).setBundlingStrength(double)public void setBundlingStrength(double bundlingStrength)
The strength controls how tightly the edges are bundled and influences the shape of the curves of bundled edges. Low values lead to only slightly bundled edges; results will mostly show individual node-to-node connectivity information. High values show the connectivity on a higher level, strongly bundling edges together and generating highly curved edge paths.
The bundling strength is defined as a value from the interval [0,1].
EdgeBundlingStage, to obtain results
with clearly observable larger bundles, it is recommended to use a strength value of 0.8 or higher.
For the EdgeBundlingStage, it is recommended to use a value, close to 0.4.0 leads to straight-line edges where edges are basically not bundled.EdgeBundlingStage, high values can significantly affect the
performance of the algorithm, especially for large graphs.bundlingStrength - the bundling strength between 0 (no bundling) and 1 (strongly
bundled edges).
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException - if the given strength is less than 0 or greater than 1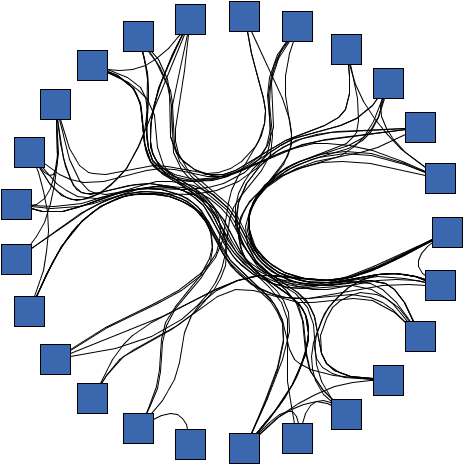 0.95 (using CircularLayouter) | 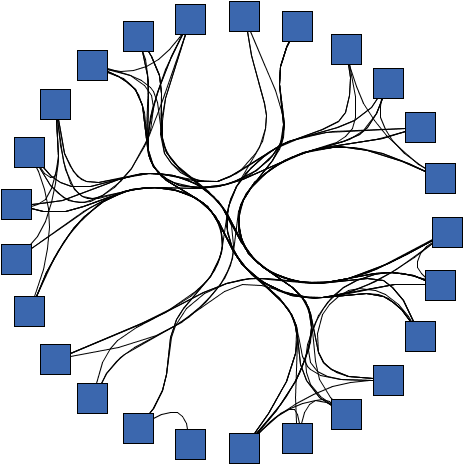 1.0 (using CircularLayouter) |  0.8 (using CircularLayouter) | 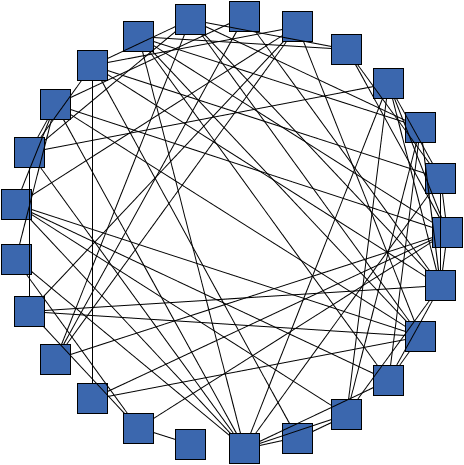 0.0 (using CircularLayouter) |
public EdgeBundleDescriptor getDefaultBundleDescriptor()
EdgeBundleDescriptor used for all edges which do not have a specific
descriptor assigned via a DataProvider registered with key EDGE_BUNDLE_DESCRIPTOR_DPKEY.
EDGE_BUNDLE_DESCRIPTOR_DPKEY,
setDefaultBundleDescriptor(EdgeBundleDescriptor)public void setDefaultBundleDescriptor(EdgeBundleDescriptor defaultBundleDescriptor)
EdgeBundleDescriptor used for all edges which do not have a specific
descriptor assigned via a DataProvider registered with key EDGE_BUNDLE_DESCRIPTOR_DPKEY.
EdgeBundleDescriptordefaultBundleDescriptor - the default descriptor responsible for edges with no specific descriptor
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException - if the given descriptor is nullEDGE_BUNDLE_DESCRIPTOR_DPKEY
|
© Copyright 2000-2025, yWorks GmbH. All rights reserved. |
||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | ||||||||
| SUMMARY: NESTED | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | ||||||||